liver gall bladder pancreas history Flashcards
(68 cards)
what are some compounds the liver makes
- albumin
- prothrombin
- fibrinogen
- lipoproteins
what hormone does the liver make?
insulin like growth factor
is the connective tissue of liver visible in humans?
not really, CT is very thin; the only time it would be visible is during pathology –> especially fibrosis
sinusoid
- discontinuous capillary in liver (also in spleen and bone marrow)
- huge openings to pass material
- have fenestrae but are not fenestrated because no continuous basal lamina
- supported by reticular fibers
hepatocytes
- liver cells surrounded by sinusoids
- long lived
- can regenerate!
- supported by reticular fibers
SER of liver
- has enzymes that are important for carb metabolism
- also for detoxification of barbituates, steroids, alcohol
- role in synthesis of lipproteins, cholesterol, bile salts and VLDL
- site of the microsomal ethanol-oxidizing system (MEOS)
role of RER in liver
- make plasma protiens
- make albumin, lipoproteins (VLDL and LDL)
- makes glycoproteins = transferrin, prothrombin, fibrinogen, non-immune globulins
- alpha 2 globulin = angiotensinogen
- ADH pathway
albumin
- contributes to colloid osmotic pressure of plasma
- transports FA, thyroid hormones, steroid hormones, substances not soluble in plasma
fxn golgi
- glycosylation of secretory proteins
- sorting of lysosomal enzymes
space of disse
separates the hepatocyte plates (“plates of cells” from the blood sinusoidal space)
what does a decrease of liver albumin (during liver disease) cause?
because albumin contributes to the maintenance of plasma oncotic pressure (“colloid osmotic”), a decr in albumin during liver failure would cause edema and ascitis
(there are not enough proteins in the blood so water flows into interstitial space )
how can you distinguish SER in liver?
- the SER in liver is notable for clusters of glycogen molecules (PAS stain!) which represents the glucose reserve for maintenance of blood sugar
- [note that glycogen is also stored in muscle]
- SER also involved in detox
- enzymes that detoxify drugs are in mem of SER
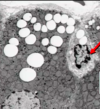
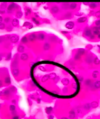
Identify

Gilsson’s capsule
trichrome stain shows the CT capsule
note that some CT goes through liver parenchyma
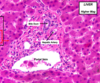
portal lobule
describes bile flow
“triangle” that describes the part that secretes bile that drains into the protal triad
- central vein at corner
- portal triad at center
hepatic acinus (portal acinus)
smallest fxnal unit in parenchyma of liver
end of long axis is central vein
end of short axis is portal triad
what types of collagen is contained in space of disse
I, III and IV
Kupffer cell
macrophage of liver
where does side chain cleavage for steroid hormone synthesis take place?
mitochondria
.
cholesterol–>pregnenolone via cholesterol desmolase
how does rer stain
basophilic
where are the enzymes involved in making steroid hormones, and those synthesizing and breaking down glycogen found ?
smooth endoplasmic retigulum
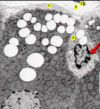
Identify

Lysosome
- hydrolyic enzymes formed in RER and are found here
- enzymes have termianl mannose-6-phosphate group that marks the m to be packaged in lysosomes
- primary lysosomes are homogenous with electron dense contents
- has a proton pump to maintain acidic interior
block 4 specific info: lysosomes release the enzyme that is responsible for break down of bone during remodeling (by osteoclasts)
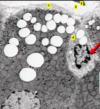
Identify
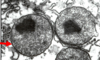
Peroxisome
- site of beta oxidation of LCFA (in addition to mitochondria)
- degrade hydrogen peroxide, a product of oxidative rxns
- Generate H2O2 = oxidase
- Break down H2O2 = catalase
- Synthesize cholesterol, plaminogens
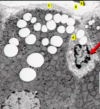
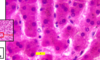
What is outlined in red?

SER
site of synthesis and breakdown as needed of glycogen
note that the red arrow is pointing to glycogen shown as cluster of indv particles
catalase
enzyme found in peroxisomes that breaks down H2O2 into oxygen and water
this is breaking downt the hydrogen peroxide that was generated by oxidases in the peroxisome