Bugs + Drugs Flashcards
(51 cards)
which species of bacteria grow hyphae
nocardia and actinomyces
these are both gram positive rods, so to differentiate,
nocardia is aerobic, actinomyces is anaerobic
mn: they are gram pos. because they have the “addition” of hyphae.

cryptococcus
commonest cause of fungal meningitis
Risk factors:AIDS; Exposure to pigeon droppings
Diagnostics: Cryptococcal antigen testing via latex agglutination; CSF gram staining: India Ink (clear halo)
characterize West Nile Virus
enveloped +ssRNA
characterize HSV encephalitis
enveloped, dsDNA, spherical
associated with temporal lobe hemorhagic necrosis
bimodal age distribution, with peak distribution at
early childhood and 50+, ages
what are the vaccine preventable causes of brain infections?
N. meningiditis and Japanese B virus

Coccidioides immitis
which CBS infectious pathogen enters via the trogan horse method (i.e intracellularly via phagocytosis)
listeria monocytogenes
best way to detect viral meningitis
Many tests can help to differentiate viral from bacterial meningitis; however, a viral polymerase chain reaction is the most accurate test. This test detects viral genetic material.

Neisseria meningitidis
characterize neisseria meningitidis
gram neg aerobic diplococci
glucose and maltose fermenting
osidase +
non-hemolytic
likes CO2
mn: Neisseria is Neg.
what is the most common cause of septic meningitis with a hypotensive patient
N. meningitidis (also look for petuchial rash)
abx for: Listeria, N. meningitidis, Strep, E. coli (sensitive)
ampicillin
empiric abx for non-infant meningitis
vancomycin, ceftriaxone, Cefepime (or cefotaxime)
+ampicillin if 50+ yo or immunocompromised
what drug would cover all of these:
Pseudomonas, N. meningitidis, E. coli, H. influenzae, Strep, Staph (sensitive)
cefepime
What is the most common means for drug entry
into the CNS?
transcellular diffusion (Small, lipophilic molecules)
CYP expression in the brain is High or low?
LOW, meaning that it does not appreciably affect drug metabolism
instead, Instead, drugs get “pumped
out” by ATP Binding Cassette
ABC Transporters such as P-gp, MRP1, MRP2, MRP3, and BCRP
Amphetamine MOA
- Displaces monoamines from vesicles
- Reverses direction of monoamine reuptake transporters
- Inhibits metabolism of monoamines by the enzyme, MAO-A
result= increased Monoamine in synaptic cleft
tranexamic acid MOA and indication
synthetic derivative of the amino acid lysine and binds the 5 lysine binding sites on plasminogen. This inhibits plasmin formation and is therefore antifibrinolytic. Indicated for intracranial hemorrhage
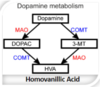
Tolcapone MOA and indication
inhibits conversion of L-DOPA into its metabolite 3-OMD –> increases conversion to dopamine instead
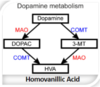
Rasagiline MOA and indication
inhibits MAOb which converts Dopamine –> DOPAL
increases CNS levels of dopamine for PD

how do Gabapentin, L-DOPA, and Vinca alkaloids cross the BBB
Protein Carriers GLUT, MCT1,
L-DOPA, –> LAT1
Heroin MOA
Presynaptic: inhibits voltage gated calcum channels (decrease neurotransmitter release)
Postsynaptic: opens K+ channels (K efflux –> hyperpolarization)
Cocaine MOA
- Blocks voltage-gated Na+ channels
- Inhibits monoamine reuptake
what would CSF studies reveal in TB meningitis
very low glucose levels
high proteins
lymphocyte predominance
(basically, it shares features of both bacterial and viral infection)