Cardiac Flashcards
(36 cards)
What are common side effects associated with Beta Blockers?
Edema Worsening HF Hypotension Fatigue Bradycardia
Rhythm?
Treatment?

Asystole
Epinephrine and Atropine
Identify Rhythm?
Symptoms?
Tx?

Premature Ventricular Contractions
Lack of cardio output
CPR, ACLS, Epi, Vasopressin, Intubation
Identify # 6
Time?
Whats happening?

QT interval
0.34-0.43
Time for entrie electrical depolarization and repolarization of the ventricles.
What do diuretics do for cardiac function for the HF patient? Acute
- Reduces venous pressure, 2. Volume returning to the LV, 3. Increase Cardiac output, 4. decrease pulmonary pressure, 5. improves gas exchange.
Why use an ACE-inhibitor for the treatment: Chronic HF 2 reasons
- They are the drug of choice for blocking the RAAS system in HF patients with systolic failure. 2. Decrease the development of ventricular remodeling by inhibiting ventricular hypertrophy.
What benefits are associated with the use of ACE-inhibitors?
Reduction of systemic vascular resistance. Increased CO Diuresis is enhanced
Rhythm?
Symptoms?
Treatment?

Sinus Bradycardia
Pale cool skin, hypotension, weakness, agina, dizziness, syncope, SOB, confusion, disorentation
Tx: Atropine if symptomatic
What are the common side effects of ACE-inhibitors?
Hypotension intractable cough hyperkalemia angioedema renal insufficiency
Why give Vasodilators to the HF patient? Acute
- They reduce circulating blood volume, 2. dilates coronary arteries. 3. Decreases preload, 4. reduces after load, 5. Increases myocardial oxygen supply.
How do you position the Acute decompensated Heart failure patient whose experiencing Dyspnea?
In high fowlers position with feet horizontal or feet dangling at the bedside.
Why are diuretics given to the HF patient? Acute
Treatment of fluid volume overload
How do Vasodilators Nitrates work?
They cause vasodilation by acting on the smooth muscle of the vessel wall. They promote vasodilation of the coronary arteries.
What medication is contradicted with use of Nitrates that could cause systemic hypotension?
Erectile dysfunction medications.
What are the problems associated with taking diuretics for treatment for Chronic HF
Reduction of potassium levels ototoxicity allergic reaction from the sulfa
Rhythm?
Whats seen?
Treatment?

Ventricular Tachycardia
Rapid HR with wide QRS complexes
Pulse: 150mg Amiodarone
Pulseless: CODE, Amiodarone, Lidocaine, defibrillation,
Rhythm?
Symptoms?
Treatment?

PAC
Distorted P-wave
Remove source, beta blockers
Identify #1
Time?
What does it mean?

P-wave
0.06-0.12
Atrial depolarization (Contraction) time
Rhythm?
Symptoms?
Treatment?
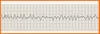
Ventricular Fibrillation
Unresponsive, pulseless, apneic
Tx: CPR, ACLS, Defibrillation, Epi, vasopressin
How do ACE-inhibitor work?
They block the enzyme responsible for covering Angiotension-1 to Angiotensin-2. Resulting in Vasodilation and excretion of Sodium.
What effects do Positive Inotropes have for treatment of chronic HF?
They increase the force of cardiac contraction They also decrease the HR Allows more complete emptying of the ventricles Reduces volume remaining in ventricle during diastole Increases CO
Rhythm?
Symptoms?
Treatment?

Atrial Flutter
Saw toothed p-waves, HR: 75-175
Unstable: cardioversion
Stable: Beata blocker, Ca2+ channel blockers
Rhythm?
Symptoms?
Treatment?

Sinus Tachycardia
HR 101-200 BMP
Remove underlying cause, IV beta blockers, Calcium channel blockers
Identify # 5
Time?
Whats happening?

T wave
0.16
Time for ventricular repolarization
*should be upright*






