Cardio Flashcards
(81 cards)
EMERGENCY DDx for Chest Pain - 7
PAPA PEP!
- PE
- ACS (STEMMI vs Unstable angina–>NSTEMMI) - [CHEEST CCC] w/u
- PTX/tension PTX
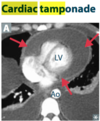
- Aortic dissection
- Pericarditis/myocarditis
- Esophageal rupture
- Peptic ulcer rupture
Unstable angina progresses to an NSTEMMI
What is Levine sign
pt puts clenched fist to chest to describe MI
What are historical features that point to ACS/MI - 8
- Onset: gradual
- Quality: Crushing, Squeezing, Tight, Pressure
- Region
- Radiation: Substernal/Radiates
- Timing: Pain between 30min - 3hours
- AssociatedSx: Diaphoresis, Apprehension, NV
- Previous: Yes
- Fam hx of 1st degree male relative with ACS at ≤ 50 yo
Common Causes of Chest Pain are usually CRGMP
Describe the Cardiac Causes -6
CRGMP
- ACS (Unstable,Stable,Prinzmetal Variant, MI)
- Cocaine - DONT GIVE BETA BLOCKERS
- Pericarditis
- Aortic Dissection
- Valvular
- [Non-ischemic Cardiomyopathy]
CRGMP = Cardiac/Respiratory/GI/Msk/Psych
Common Causes of Chest Pain are usually CRGMP
Describe the Respiratory Causes -5
CRGMP
- PE
- PNA
- Pleurisy
- PTX
- Pulm HTN/Cor Pulmonale
CRGMP = Cardiac/Respiratory/GI/Msk/Psych
Common Causes of Chest Pain are usually CRGMP
Describe the Gastrointestinal Causes -5
CRGMP
- GERD
- PUD
- Esophageal (dysmotility, inflammation, rupture)
- Pancreatitis
- Biliary (cholecystitis, cholangiits)
CRGMP = Cardiac/Respiratory/GI/Msk/Psych
Common Causes of Chest Pain are usually CRGMP
Describe the Musculoskeletal Causes -4
CRGMP
- Costochondritis
- Rib Fracture
- Muscular strain
- Herpes Zoster
CRGMP = Cardiac/Respiratory/GI/Msk/Psych
Common Causes of Chest Pain are usually CRGMP
Describe the Psychogenic Causes -2
CRGMP
- Panic DO
- Hyperventilation
CRGMP = Cardiac/Respiratory/GI/Msk/Psych
Which demographics tend to present with ACS/MI in an atypical way? - 3 ; What sx would you expect with them?-5
Women / Elderly / Diabetics
- only SOB
- only NV
- Palpitations
- syncope
- complete cardiac arrest!
chest pain may or may not be present in these populations
When is Angina classified as Unstable -3
when chest pain is…
- > 20 min or ⬆︎in frequency
- New
- occurs at rest
When it Nitroglycerin contraindicated? - 2
- Pt took Phosphodiesterase inhibitors within last 24 hours
- Inferior wall MI
What therapies are used to treat ACS?-7 ; how do these help with ACS?
use CHEEST CCC for ACS workup
Pts with ACS Need OBAMAA!
- NTG 0.4mg q5min x ≤3 = VasoDilates Veins and Coronary Arteries
- Oxygen = Minimizes ischemia
- Beta Blockers = ⬇︎ HR –> ⬇︎O2 demand AND⬇︎ Arrhythmia risk
- [ASA325 and Heparin] = limits thrombosis
- Morphine = Pain
- ACEk2 inhibitors within 24 hrs= ⬇︎ [L Ventricle Dilation/Remodeling]
- AtorvaSTATIN - comes later
Careful: ASA and Beta blockers can –> asthma exacerbation
Contraindications to giving beta blockers - 9
- HR < 60
- Systolic BP < 100
- 2nd or 3rd degree heart block
- LV dysfunction
- COPD severe
- Asthma severe
- peripheral hypOperfusion
- PR > 240
- MI secondary to Cocaine
How long does it take Myoglobin cardiac biomarker to
Rise?
Peak?
Return to Baseline?

How long does it take Troponin cardiac biomarker to
Rise?
Peak?
Return to Baseline?
Troponin iiiii is the most sensitive

How long does it take Creatine Kinase cardiac biomarker to
Rise?
Peak?
Return to Baseline?

[Atrial Fibrillation] is the most common tachyarrhythmia. It is often precipitated by what 4 things?
“Smh, SAME Afib as before!”
- Acute Systemic Illness (Hyperthyroid / HF / HTN)
- Sympathetic Tone INC (Hyperthyroid/CHF/Exercise)
- EtOH in excess
- Mitral Stenosis
What dose of Beta Blockers should be given for ACS?
Pts with ACS Need OBAMAA!
Metoprolol 5mg q5min x ≤3 =(with goal of) 60bpm
Careful: ASA and Beta blockers can –> asthma exacerbation
What dose of Morphine should be given for ACS?
Pts with ACS Need OBAMAA!
Morphine IV 2-10mg q5-15min
Careful: ASA and Beta blockers can –> asthma exacerbation
What dose of Nitroglycerin should be given to pts with ACS?
Pts with ACS Need OBAMAA!
NTG 0.4mg q5min x ≤3
Careful: ASA and Beta blockers can –> asthma exacerbation
Describe the system used to diagnose and assess for DVT
Wells Criteria!

List the contraindications to using Thrombolytics for STEMMI ACS - 6
- Intracranial hemorrhage hx
- Aortic dissection
- Active bleeding
- Closed head or facial trauma within preceding 3 mo
- Brain CA
- AVM
What is the TIMI Risk Score for STEMI used for? ; What are the components? - 9

Reperfusion therapy is given for STEMI within __ hours of chest pain onset. What are the 2 options?
12
- PCI preferred if within 90 minutes and if CardioShock is present! -otherwise use Thrombolytics
- Thrombolytics (“__plase”)
* PCI = PerCutaneous Intervention*