Trauma Flashcards
(15 cards)
GCS(Glasgow Coma Scale) predicts Prognosis of what 4 things?
The 3 components are EVM (Eyes/Verbal/Motor)
Describe the [Verbal Response] component (5)
Coma / Bacterial meningitis / Brain Trauma / SubArachnoid Hemorrhage
EVM = Eyes / Verbal / Motor

GCS(Glasgow Coma Scale) predicts Prognosis of what 4 things?
The 3 components are EVM (Eyes/Verbal/Motor)
Describe the [Eye Opening] component (4)
Coma / Bacterial meningitis / Brain Trauma / SubArachnoid Hemorrhage
EVM = Eyes / Verbal / Motor

GCS(Glasgow Coma Scale) predicts Prognosis of what 4 things?
The 3 components are EVM (Eyes/Verbal/Motor)
Describe the [Motor Response] component (6)
Coma / Bacterial meningitis / Brain Trauma / SubArachnoid Hemorrhage
EVM = Eyes / Verbal / Motor

GCS(Glasgow Coma Scale) predicts Prognosis of what 4 things?
The 3 components are EVM (Eyes/Verbal/Motor)
What is the interpretation for the GCS results?
Coma / Bacterial meningitis / Brain Trauma / SubArachnoid Hemorrhage
EVM = Eyes / Verbal / Motor
SEVERE < (Moderate 8 - 12) > minor

When interviewing a sexual assualt victim, what are the questions that should be asked? - 7
- Who did it (if they know)?
- What what happened (what kind of assault)?
- When was last menstrual period, last consensual intercourse, last OCP usage?
- When did this happen?
- Where are your areas of pain?
- Where did this happen?
- How many people were involved?
Semen can be found with Wood’s fluorescent lamp
what is the management for a sexual assult victim - 8
- Address all physical injuries (admit prn)
- Tetanus px
- HepB px
- GC/Chlamydia px
- HIV counseling and px if elected
- STD and pregnancy testing
- Med and Psych f/u within 2 weeks
- Social worker f/u to ensure safe place to discharge
What are the reversible causes of cardiac arrest? - 10
5 H’s and 5 T’s
- HypO/hyperKALEMIA
- HypOthermia
- HypOvolemia
- HypOxia
- Hydrogen ions (acidosis)
- Tension PTX
- Tamponade cardiac
- Toxins (OD)
- Thrombosis pulmonary
- Thrombosis corornary
Also check for hypOglycermia
How should you manage Bradycardia with a pulse?
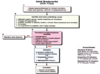
How should you manage Tachycardia with a pulse?

During CPR at what rate should compressions be delivered? ; how deep should compressions be?
≥100/min ; ≥2 inches (or 5 cm) deep
Rotate compressor q2 min
If IV or IO access has not been successfully established, some meds can be given via the Endotracheal tube!
What is the dose adjustment for the ET tube? ; Which drugs are these? - 5
original dose x 2
NAVEL
- Naloxone
- Atropine
- Vasopressin
- Epinephrine
- Lidocaine
When should you STOP giving combined BLS and ACLS resuscitation efforts?
after 20 minutes
Initating hypothermia after a pt has returned to spontaneous circulation involves cooling down to ___ °C for ___ hours helps out-of-hospital cardiac arrest when dysrhythmia is ____ only
32C (89.6F) ; 12-24 hrs ; VTach/VFib

Must be Adult, mechanically ventilated, ≤60 min needed to return spontaneous circulation
How do you convert Farenheit to Celsius? - 2
F to C = MD (Minus, and then Division)
- F - 32 = x
- x ÷ 1.8 = Celsius
How do you convert Celsius to Farenheit? - 2
C to F = XF (x as multiplication and Farenheit needs 32)
- C x 1.8 = o
- o + 32 = Farenheit


