EKG Flashcards
(21 cards)
etx for Wolf Parkinson White syndrome?
Wolf Blitzer Drives With Style
accessory electrical pathway between the atria and vt enables early ventricular activation –> SVT and cardiogenic shock

PSVT is a ____(regular/irregaulr) rhythm with a rate usually of ______. It is also referred to as _______
regular ; 150-250 bpm ; AV nodal reentrant tachycardia
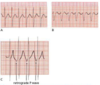
V1: little blip in QRS (representing superimposed retrograde P wave)
PSVT is a ____(regular/irregaulr) rhythm with a rate usually of ______. It is also referred to as _______
What are EKG signs of PSVT? - 4
regular ; 150-250 bpm ; AV nodal reentrant tachycardia
- No p waves (indicates rhythm does not start from SA node or ectopic atria - even though it could!)
- narrow QRS (indicates rhythm does not start from vt themselves)
- Tachycardia (because of the AV nodal reentrance)
- +/- retrograde P waves (from reentry impulses depolarizing atrial from below)
tx: vagal manuevers ⬇︎ SA AND AV node conduction –> adenosine to identify the arrhythmia
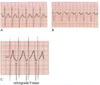
If there are ___ Big boxes between each R wave, what is the HR?
3
4
5
3 BIG boxes between each R = 100 bpm
4 = 75
5 = 60
300/# of BIG boxes between each R
PSVT is a ____(regular/irregaulr) rhythm with a rate usually of ______. It is also referred to as _______
Tx for breaking PSVT - 5
regular ; 150-250 bpm ; AV nodal reentrant tachycardia
- Vagal manuevers
- Adenosine
- BBlockers
- CBlockers
- electrical cardioversion
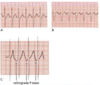
[T or F] you can use vagal manuevers to terminate atrial flutter
Why or why not?
FALSE ; atrial flutter originates above the AV node (in the atria). Vagal manuevers only retard SA/AV node conduction, so it would allow you to see the p wave more for diagnosis but not terminate it

Contraindication to Adenosine usage
bronchospastic lung disease
RRAIB MC
Describe the EKG for 1st degree AV Block
MOD?
Mngmt?
PR > 200 ms
Constant Prolonged conduction of atrial impulses
No further w/u or tx
small box = 40 ms
RRAIB MC
Describe the EKG for [Mobitz 2-2nd degree] AV Block
HAS A WORST PROGNOSIS THAN MOBITZ 1 WB-2ND DEGREE
Random beat drop (loss of AV conduction) with NO CHANGE TO PR interval

- small box = 40 ms*
- HAS A WORST PROGNOSIS THAN MOBITZ 1 WB-2ND DEGREE*
RRAIB MC
Describe the EKG for 3rd Degree AV Block
Causes?-2
Mngmt? - 2
No correlation between P and QRS (complete AV dissociation)
Idiopathic fibrosis vs Congenital
Sx = Tachypnea, SOB, cyanosis
Mngmt:
- Immediate pacemaker (transQ vs transvenous)
- ABCs + O2 + monitor
small box = 40 ms

RRAIB MC
What are the main causes of AV Blocks? - 7
- Age
- Ischemia
- Cardiomyopathy
- Myocarditis
- Congenital
- Surgery
- Valvular

Name 3 EKG Signs of Atrial Fibrillation
- [irregularly irregular R-R intervals] (the already irregular R-R interval will occur at an irregular pace since atrial electrictivity is chaotic)
- Absent or [low-amp fibrillatory] P-waves
-
Narrow QRS Complexes
* Causes = PIRAATES*

Infarcts in these areas of the heart is indicated on EKG by [ST Elevations] or [Q waves] in which leads?
Anterior MI
Septal MI
Which leads should you expect reciprocal ST depression for these areas?

RRAIB MC
Describe the EKG for [Mobitz 1 Wenckebach 2nd degree] AV Block
Progressive PR prolongation until there’s a beat drop (loss of AV conduction)
small box = 40 ms
How can Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia be differentiated from Atrial fibrillation?
Even though they vary in shape, the P waves will be discernible (since they aren’t fibrillating)
P waves with ≥3 different morphologies = MAT
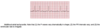
What is Bigeminy?
when there is 1 beat for every 1 PVC
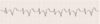
Trigeminy = 2 beats: 1 PVC
When are Premature Ventricular Contractions considered malignant (likely to cause VTach/VFib)? - 4
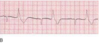
- ≥3 PVCs in a row (since this = VTach)
- different appearing PVCs (means they come from different areas)
- PVCs that fall on the T wave (R on T) - image
- Any PVC occuring in setting of MI

Torsade de pointes is a form of ____[VTach/VFib] that is usually seen in ____ intervals
Why is it associated with these type of intervals usually?
VTach ; Prolonged QT intervals
Because when a PVC falls during a prolonged T phase (falls during prolonged repolarization) it can precipitate [Torsade de pointes VTach]
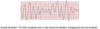
What is sick sinus syndrome
AKA bradytachycardia syndrome
alternating episodes of SVT (i.e. class PSVT or aFib) and bradycardia with long pauses in between ( a few Vt escape beats may occur during this time)
Tx = pacemaker

Infarcts in these areas of the heart is indicated on EKG by [ST Elevations] or [Q waves] in which leads?
Inferior MI
Lateral MI
Which leads should you expect reciprocal ST depression for these areas?

Infarcts in these areas of the heart is indicated on EKG by [ST Elevations] or [Q waves] in which leads?
Posterior MI
R Ventricular MI
Which leads should you expect reciprocal ST depression for these areas?



