Cardiovascular Flashcards
(38 cards)
Definition of AAA
Permanent dilatation of >3 cm (i.e. 1.5x)
Most sensitive and specific imaging for AAA
U/S
Indications for open AAA repair
Large (≥5.5 cm) Expanding at ≥1 cm/year Symptomatic
Types of aortic dissection
DeBakey: 1 - ascending + arch + descending 2 - ascending 3 - descending Stanford: A - ascending B - descending
Radiation of pain in ascending vs. descending aortic dissection
Ascending - anterior Descending - interscapular
Management of aortic dissection
Fluids, oxygen, beta blockers, morphine, surgical repair, post-op antihypertensives
Indications for surgical repair of aortic dissection
Type A Type B with persistent pain or branch occlusion
ECG findings in cardiac tamponade
Low voltage QRS, electrical alternans, PR depression
Indications for carotid endarterectomy
Symptomatic ≥70% stenosis Symptomatic 50-70% stenosis (less benefit) Asymptomatic ≥70% stenosis (debated)
Bifascicular block
LAD + RBBB
Trifascicular block
LAD + RBBB + 1st degree heart block
Rate control for AF
Beta blocker (atenolol, metoprolol) Non-dihydropyridine CCB (verapamil, diltiazem) Digoxin - in heart failure
Rhythm control for AF (cardioversion and maintenance)
Cardioversion: DC cardioversion Flecainide + beta blocker Amiodarone Maintenance: Flecainide Sotalol Amiodarone
Management of SVT (AVNRT/AVRT)
Vagal manoeuvres Adenosine Verapamil Catheter ablation
Management of VT/VF
DC defibrillation Amiodarone Lignocaine
Management of heart block
1 - none 2 (Mobitz I) - none if asymptomatic, atropine if symptomatic 2 (Mobitz II) - pacemaker 3 - pacemaker
ECG findings in SVT
Delta wave, small P wave, short PR interval
Management of asystole/PEA
Adrenaline
ECG findings in HOCM
ST depression, tall QRS, T wave inversion
Management of HOCM
Symptomatic relief - BBs, CCBs Surgical myectomy
Morphological changes in MI
12-24 hours - dark mottling
1-3 days - mottling + yellow-tan centre
3-7 days - yellow-tan centre + hyperaemic borders
7-10 days - maximally yellow-tan + depressed red-grey borders
10-14 days - depressed red-grey borders
2-8 weeks - grey-white scar
>2 months - complete scarring
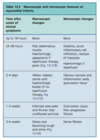
ECG changes in MI

ABI values in PVD
Normal >1.0
Intermittent claudication 0.5-1.0
Critical limb ischaemia <0.5
Signs of aortic stenosis
Ejection systolic click
Soft S2
S4 heart sound
Carotid parvus et tardus
Narrow pulse pressure