Ch. 12 Flashcards
(109 cards)
Types of neuroglia aka glial cells (found in CNS):
Bank: Microglia, Ependymal cells, Oligodendrocytes, Schwann Cells, Astrocytes, Satellite Cells
Description:
- Star-shaped cells with many processes
- Metabolize NT’s, maintain [K+] balance for CNS neurons
- Help form the blood-brain barrier (BBB)
- Serve as link between neurons & blood vessels
Nutshell: Maintains environemnt for neurons, which involves balancing POTASSIUM

Astrocytes

_______ = two or more graded potentials added together creates a greater change in membrane potential
Summation

Types of Neurotransmitters associated with CNS & PNS:
Acetylcholine is the most ______ of the neurotransmitters. It exists in both the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. It’s also excitatory (i.e. moves muscles) and inhibitory (i.e. slows heart rate)
versatile
Graded potential is
- Generated on _______ (axons/membrane of dendrites and cell body)
- Remains localized; _____ (short/long)-distance communication only
membrane of dendrites and cell body
short

Quiz: Which items fit “Graded Potential” vs “Action Potential”


____________ - small deviation from RMP caused by a certain stimulus
_______________ GP – inner membrane more negatively charged than normal RMP
_______________ GP – inner membrane less negatively charged than normal RMP
Graded Potential
Hyperpolarized
Depolarized
NOTE: Occurs due to the opening/closing of mechanically or chemically gated channels (not voltage gated)
When ions move thru these gated channels, the membrane either depolarizes OR hyperpolarizes (relative to RMP); depends on ion charge & flow direction

Faulty neurotransmitters are treated in 2 ways:
1) With drugs that _____ a NT
2) Drugs that ______ a transmission
mimic
block
Types of Neurotransmitters associated with CNS & PNS:
_____ Acids
• Excitatory CNS: Glutamate & Aspartate
• Inhibitory CNS: GABA (brain) & Glycine (spinal cord)
Amino
Types of Ion Channels: Chemically-Gated, Voltage-Gated, Mechanically-Gated, Leak Channels
- Not gated
- Randomly Open/Close
- Membrane more permeable to K+ than Na+
- More K+ leak channels and are leakier than sodium
- Found in nearly all areas & types of neurons
Leak Channels
Nervous system serves 3 basic functions that relate to maintenance of an internal balance called ___________
What are those 3?
homeostasis
- Sensing changes, both inside & outside the body (sensory function)
- Interpreting these changes (integrative function)
- Reacting to these changes by causing muscle contractions or glandular secretions (motor function)

Neurotransmitters are _____ (slowly/quickly) removed from the synaptic cleft by:
- ______ out of (away from) the synaptic cleft
- Enzymatic degradation (e.g. acetylcholinesterase)
- Uptake into cells – ______ transported back into neurons (reuptake) or into neuroglia (uptake)
quickly
- Diffusion
- actively
Branch of medical science that deals with nervous system is ___
neurology
Types of Ion Channels: Chemically-Gated, Voltage-Gated, Mechanically-Gated, Leak Channels
- Gate opens in response to neurotransmitters, hormones, and some ions
- • Found in dendrites of some sensory (pain) neurons, interneurons, & motor neurons
Chemically-Gated
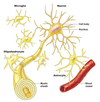
What are nerve cells called?
Neurons
Other factors that can modify of membrane potential:
- Increased excitability - reduce the threshold; easier to depolarize membrane
- Alkalosis (pH > 7.45) - lightheadedness, tingling, numbness spasms, etc.
- Caffeine & nicotine
- Decreased excitability – increases threshold; more difficult to depolarize
- Acidosis (pH < 7.35) - weakness, lethargy, coma
- Hypnotics, tranquilizers, anesthetics
just look at this a few times
The PNS is divided into 3 “subdivisions”:
The _____ nervous system (SNS) is voluntary. It’s basically your muscles.
- Sensory (afferent) neurons conduct impulses from cutaneous & special sensory receptors to the CNS
- Motor (efferent) neurons send impulses from CNS to __________
Somatic
skeletal muscles
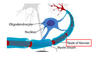
Saltatory Conduction:
• Myelin sheath = electrical insulator; blocks membrane depolarization
• Nodes of Ranvier = contains many voltagegated channels (e.g. Na+)
• Membrane depolarizes/repolarizes very _______ (slowly/quickly) at nodes
• Stops at myelin sheath
• Nerve impulse “leaps” from node to node; travels very FAST
• Also uses ______ (less/more) ATP, since only small portions of the membrane gets depolarized

Quickly
less
The word _____ means = the capability to change based on experience.
Repeat to yourself: Learning new things means making new connections! Expending the dendrites to connect to other neurons (and using your neurons!). i.e, repitition is the best way to learn).
Plasticity
Repeat to yourself: Learning new things means making new connections! Expending the dendrites to connect to other neurons (and using your neurons!). i.e, repitition is the best way to learn).
In the CNS, there is no connective tissue between nerve fiber bundles; therefore, bundle of nerve fibers (axons) are called a _____ instead of a nerve.
tract
Two basic types of synapses:
- Electrical synapse - found in smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, CNS (between neurons)
- _____ (one-way/two-way) communication between cells:
- • Ionic current spreads directly from cell to cell thru ____ junctions
- • Electrical synapses are ____(faster/slower) than chemical synapses
- • Quickly coordinates (synchronizes) activity of a group of
- neurons or muscle fibers (e.g. in heart, bladder, etc.)
two-way
gap junctions
faster

Myelination ________(decreases/increases) from birth to maturity (e.g. better coordination with time)
increases
Excitatory & Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential:
Excitatory NT - __________ (hyperolarizes/depolarizes) the postsynaptic neuron membrane
- Inner membrane less negative; Cations IN or anions OUT
- Generates _______ (excitatory/inhibitory) postsynaptic potential (EPSP) – closer to threshold potential
- A single EPSP is not enough to start a nerve impulse. However, it is more excitable (closer to its threshold). The next EPSP may be enough to start a nerve impulse (summation).
depolarizes
excitatory
A bundle of nerve fibers in the PNS is called a nerve.
A bunde in the CNS is called a tract because it doesn’t have __________ surrounding it
nerve
connective tissue
Which cell produces the lipids and mylinates the axon?
Schwann cell