Chapter 12 part 2 Flashcards
(20 cards)
A stimulus is defined as what?
any change in environment that is strong enough to create and action potential
action potential is what and how does it travel?
nerve impulse and it travels rapidly and at constant strength
neuroglia are the support cells of the CNS what are their functions
form the blood brain barrier, form the myelin sheath, makes the CSF, participates in phagocytosis
Neurons can range in shape, how small or large can they be
from 5 um up to 135um
Although Neurons can be different size and shapes they will all have these same structures
A cell body, an axon, a dendrite, and axon terminals
what is the function of dendrites?
receive conduct impulses toward the cell body
the cell body contains many organelles but one type of apparatus is missing, what is it
no Mitotic apparatus
what are three structures that lie between the cell body and the axon of a nerve
the axon hillock: where the axon and body fuse the
initial segment: the beginning of the axon the
trigger zone: junction between the hillock and initial seg
telodendria are
axon terminals
what is the site of communication between neurons and other cells called? what is the gap between them called?
Synapse and synaptic cleft
there are 4 types of neuroglia in the CNS what are they
Astrocytes: maintain the chemical enviro Oligodendrocytes: produce myelin Microglia: phagocytes Ependymal cells: form + circulate CSF
the PNS only has 2 types of Neuroglia what are they
Schwann cells: produce myelin Satellite cells: provide structural support, regulate material exchanges between cell bodies and interstitial fluid
where does nerve regeneration happen? and what cells is it largely dependent on?
in the PNS only and its dependent on Schwann cells
the Neurolemma is what? and how does it contribute to nerve regeneration?
the outer nucleated cytoplasmic layer of schwann cells, forms the regeneration tube that guides and stimulates regrowth of axon
what is the loss or destruction of myelin?
demyelination
what are the stages of nerve regeneration in relation to Schwann cells?
Dedifferentiation, removal of debris, schwann cells guide axon to target tissue, redifferentiation of schwann cells
what is Wallerian degeneration?
macrophages are recruited to assist in demyelination and phagocytosis of debris

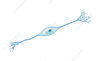
- A Multipolar neuron.
- vast majority of neurons are this type
- motor or efferent/interneurons/ most CNS
- Bipolar: denrites and cell body are not fused
- conveys the special senses of: sight, smell, hearing, balance
- found in: retinas, inner ear, olfactory areas of brain

- Unipolar: one long continous axon between dendrites and axon terminal, cell body to one side
- convey touch and stretching
- most neurons in the PNS are ths type


