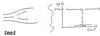Chapter 2: divergence and vorticity Part 2 Flashcards
(39 cards)
Convergence is defined as
the increase of mass within a given layer of the
atmosphere
divergence is
the decrease of mass within a given layer of the atmosphere
conditions for convergence to take place
the winds must result in a net inflow of, air into that layer
For convergence to take place, the winds must result in a net inflow of, air into that layer. This type of convergence is generally associated with
low‐pressure area
where convergence of winds toward the center of the low results in
an increase of mass into the low and an upward motion
Divergence
Winds in this situation produce
a net flow of air outward from the layer
Winds in this situation produce a net flow of air outward from the layer. We
associate this type of divergence with
high‐pressure cells
Winds in this situation produce a net flow of air outward from the layer. We associate this type of divergence with high‐pressure cells, where the flow of air is directed
outward from the center, causing a downward motion
The natural coordinate system describes
motion as normal or tangential to the radius of curvature of the flow
how is the natural coordinate system represented
Rather than isobars,
flow is depicted as streamlines, which represent the instantaneous direction of the wind, and isotachs, the instantaneous wind speed
We can construct natural coordinates with
unit vectors
We can construct natural coordinates with unit vectors
n and , where
n is the normal vector and
s is the tangential vector
k is directed vertically upward
Ψ (angle) as the angle that the tangent of the curve makes with a fixed direction, and
the radius of curvature of the flow
Note thatΨis defined as
positive in the counterclockwise direction and R > 0 for counterclockwise flow
In the natural coordinate system the direction of the unit vectors is
not constant as in the Cartesian system
In the natural coordinate system the direction of the unit vectors is not constant as in the Cartesian system, but is determined by
the direction of the wind
In natural coordinate system, the horizontal divergence can be expressed as:
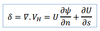
explain the components
(the first term)
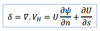
The first term, the directional divergence(convergence),represents the change in
angle with movement (or change in isobar spacing) across the flow.
explain the components
(the first term)
The first term, thedirectional divergence(convergence),representsthechangein
angle with movement (or change in isobar spacing) across the flow. occures when
winds spreading outward (inward) at a constant speed, which represents a net
outflow (diffluence), or inflow (confluence)ofair.
what is the condition of directional divergence and convergence
speed is constant in both cases
show directional divergence and convergence

the second term
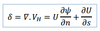
thespeed divergence(convergence), occurs when downstream winds are faster (slower) than upstream winds for the same isobar spacing. More air is moving out (in) this area than moving in (out).
condition of speed convergence and divergence
same isobar spacing
show speed divergence and convergence

According to the geostrophic relationship, which shows that
if the isobar spacing Δx remains constant, the wind speed doesn’t change