Chapter 7 Flashcards
(11 cards)
Groups:
punctuated equilibrium model:
*

Group:A group consists of 2 or more ppl interacting interdependently to achieve a common goal
- Formal Work grps: established by org to achieve org goals
- Informal grps: emerge naturally in response to common interests
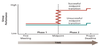
Punctuated Equilibrium Model: Describes how grps with deadlines are affected by first meeting and subsequent mid-point transitions
- Model breaks grp development process into 2 phases and emphasizes importance of midpoint transition as crucial in grp meeting its goal by deadline
Group structures and consequences:
and main structural characteristcs
Group structures and consequences: Group structure refers to the characteristics of stable social org of a grp
Structural characteristics are: Group size/Diversity of members/Group norms/Roles/Status
Group size
Group size
- Size of group has impact on task performance
- As grp size increases, indv verbal participation decreases
- Tasks may be:
- Additive: tasks in which grp performance is dependent on sum of performance of indv group members(ex: building a house)
- Disjunctive: grp performance is dependant on performance of the best member(ex research team)
- Conjunctive: tasks in which grp perfomance is limited by perfomance of poorest grp member
Diversity of members
Diversity of members
- Group diversity has strg impact on interaction patterns
- Diverse grp have more diffictult time communicating effectively and becoming cohesive
- Diverse grp might take longer to do forming, storming and norming
- Once they do develop, more and less diverse grps are equally cohesive and productive
Group norms
- Norms cover:
- How do norms develop ?
- Why Norms are enforced ?
Group norms
- Social norms: are collective expectations that members of social units have regarding the behaviour of each other
- Norms: codes of conduct that specify standards against which we evaluate the appropriateness of behaviour. Provide regularity and predictability of behaviour
- Norms cover:
- performance(work ethic, work quality, levels of tardiness)
- Appearance(personal dress, when to look busy, when to ‘‘goof off’’, how to show loyalty)
- Social Arrangement: how team members interact
- Reward allocation: pay, assignments, tools& equipment
- How do norms develop?
- Explicit grp member statements
- Critical events in grp history
- Primacy: initial patterns of behavior.
- Carryover Behaviour
- Why Norms are enforced ?
- Facilitate grp survival
- Make behaviour predictable
- Minimize embarrassment
- Express central values
- Clarify grp identify
Roles
Roles
- Position in a grp that have a set of expected behaviours attached to them
- Roles represent packages of norms that apply to particular grp members
- 2 roles in org:
- Assigned: formally prescribed by an org as a means of dividing labor and responsibility to facilitate task achievement(president software, engineer, programmer)
- emergent roles: naturally develop to meet the social-emotional needs of group members or to assist job accomplishment (class clown and office gossip informal leaders)
- Role Ambiguity: exits when goals of one job or methods of performing it are unclear
- Role conflict: When indv is faced with incompatible role expectations. Four types of role conflict:
- Intrasender Role Conflict, the guys like chill out but gives you work that necessitates immediate attention
- Intersender role Conflict,:two or more senders differ in their expectations for a role occupant Intersender role Conflic can develop
- inter-role Conflict( when you work you are expected to do several roles and sometimes these roles are incompatible)
- person role Conflict.( sometimes you simply cannot accomplish a task as not compatible with skills)
Status
Status
- Status: rank, social position or prestige according to grp members
- Represents grp evaluation of member
- What is evaluated depends of status system in question
- All orgs have Formal(tangible indicators of status) and Informal status systems
Group Cohesiveness
- Following factors contribute to group cohesiveness:
- Consequence of Cohesiveness include:
Group Cohesiveness
- Characteristic of groups that are especially attractive to their members
- Cohesiveness is relative property of groups and is informal, emergent group process
- Following factors contribute to group cohesiveness:
- Threat and competition
- Success
- Similarity of members
- Size
- Toughness of initiation
- Consequence of Cohesiveness include: Strong participation and commitment, conformity, additional success
Social Loafing
- Some ways to counteract social loafing
Social Loafing
- Tendency of withholding physical or intellectual effort when performing grp task
- Free rider: People lower effort to get free ride at expense of other grp members
- Sucker affect: People lower effort bc of feeling that other are free riding
- Some ways to counteract social loafing
- Make indv perfomance more visible
- Make sure work is interesting
- Increase felling of indispensability
- Increase performance feedback
- Reward grp performance
Teams
- Collective efficacy:
Teams
- Teams is group of people that work jointly towards common objective
- Group and team interchangable
- Collective efficacy: consists of shared beliefs tat a team can successfully perform given task
3 Types of teams

- G
- Principles for effectivenss: number of factors contribute to effectivenss of this type:
* * * * * *
- Principles for effectivenss: number of factors contribute to effectivenss of this type:
-
Virtual:
- Advantages:
- Challenges:
3 Types of teams
-
Self managed: groups generally provide members with opportunity to do challenging work under reduced supervision
- Grp responsibilities include planning and scheduling of work, assigning tasks to team members, making operational decisions and taking action on problems
-
Cross-functional: Work grps that bring people with different functional specialties together to better invent , design or deliver a product or service
- Principles for effectivenss: number of factors contribute to effectivenss of this type:
- Composition: all relevant specialties must be part of team
- Superordinate goals: attractive outcomes that can only be achieved by collab
- Physical proximity: team members located close to one another
- Autonomy
- Avoid petty rules and procedures: basic decision procedures must be laid down to prevent anarchy
- Leadership: Leaders need strong people skills in addition to task expertise to avoid team conflict
- Principles for effectivenss: number of factors contribute to effectivenss of this type:
-
Virtual: use tech to communicate and collaborate across space, time and org boundaries
- Advantages: around the clock work, reduced travel time and cost and larger talent pool
- Challenges: difficulty to establish inter member trust, miscommunication, isolation , high costs and mana issues



