CVPR Week 6: Control of ventilation Flashcards
(106 cards)
Objectives

CNS respiratory centers location
Medulla and Pons
Basic elements of the respiratory control system
7 listed
- Pain/emotional stimuli
- Higher brain centers - voluntary control
- Stretch receptors in the lungs
- Irritant receptors in the lungs
- Muscle/joint receptors in the lungs
- Central chemoreceptors
- Peripheral chemoreceptors
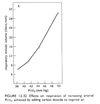
Central chemoreceptors detect?
increased CO2
increased [H+} concentration
Peripheral chemoreceptors detect?
- decreased O2
- increased CO2
- increased [H+]
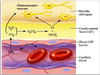
Where are central chemoreceptors
in cerebrospinal fluid and sense CO2 and H+
Where are the peripheral chemoreceptors?
carotid and aortic bodies
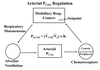
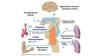
Controller of the respiratory control system
Brainstem medulla and pons respiratory centers
Sensors of the respiratory control system?
Central and peripheral chemoreceptors
Controlled variables of respiratory control system?
PaCO2
PaO2
Arterial pH
Effectors of the respiratory control system
Muscles of respiration
Identify respiratory control system components
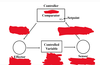
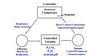
Innervation of central chemoreceptors
Direct central connections
Innervation of peripheral chemoreceptors
- vagus nerve for aortic bodies
- glossopharyngeal nerve for carotid bodies
Muscles of respiration innervation
- Respiratory somatic motor neurons
The role of the muscles of respiration in the respiratory control system
innervated by respiratory motor neurons that alter respiration to induce changes in blood gasses PaCO2, PaO2 and arterial pH
Basic respiratory rhythm generator location
Medulla
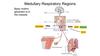
if the spinal cord is severed just below the pons but above the medulla
basic respiratory rhythm is preserved
if the spinal cord is severed just below the medulla
all breathing stops
Neurons active in the respiratory cycle
Groups of medullary neurons are active in either the inspiratory or the expiratory phase of the respiratory cycle
Medullary neurons active during inspiration
Dorsal respiratory group
When are the ventral respiratory group active
during inspiration and expiration
Dorsal respiratory group location
within the nucleus of the tractus solitarius (NTS)
The dorsal respiratory group receives information from?
receives afferent information from the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves