Dermatology Flashcards
(48 cards)
what are primary lesions
- initial eruption that developes spontaneously as a direct reflection of underlying disease
- appear quickly and disappear quickly
examples of primary lesions
macule or patch
papule or plaque
pustule
vesicle or bulla
wheal
nodule
tumor or cyst
what are secondary lesions
- evolve from primary lesions/artefacts induced by patients/external factors (trauma/biting/licking and medication)
- usually stay around for a much longer time period
which lesions can be primary or secondary
alopecia
scale
crust
follicular casts
comedo
pigmentary abnormalitites
examples of secondary skin lesions
epidermal collarette
scar
excoriation
erosion or ucler
fissure
lichenification
callus
what dis?

macule
flat spot ( <1 cm) on skin with change in skin color
what dis?

patch
= macule >1 cm
that is a type of mcule caused by bleeding into the skin
purpura, petechial, ecchymoses

a small, solid elevation in skin up to 1 cm in diameter is a _______
papule

what dis?

plaque
coalition of plaques forming flat-topped elevation
what is a pustule
small elevation of epidermis filled pus

what dis?

Vesicle
elevation of epidermis filled with clear fluid
what is a vesicle > 1 cm in diameter
bulla

sharply delineated lesion of edema is known as a ______
wheal
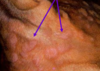
a solid raised palpable lesion > 1 cm
nodule
can include abscess (fluctuant lesion in dermis or SQ from pus)

what are these?

Nodule: Tumor
large palpable mass - Neoplastic
what is an epithelial lined cavity with solid or fluid material?
Cyst

what is alopecia?
absence of hair from area where it is normally present
what is an accumulation of loose fragments of skin
scale

what is an accumulation of dried serum/ exudate on the surface of the skin?
crust

what is an accumulation of keratin & sebaceous material stuck to a hair shaft
follicular cast
a dried hair follicle filled with debris is a ______
comedone

what is an epidermal collarette

scale arranged in a circular pattern
associated with a pustule, vesicle or bullae
linear abrasion of the skin is called ____
excoriation










