Eye Infections 2 Flashcards
(71 cards)
Discrete foci of retinitis w/white retinal or choroidal lesions can be seen in _________ (disease).
cat scratch
(microbe: bartinella hensalae)

Parinaud’s Oculoglandular syndrome is caused by _________. Presents with _______.
- Caused by cat scratch disease (Bartonella henselae)
- Conjunctivitis and neuroretinitis

Moraxella catarrhalis characteristics (3)
- Gram negative diplococci
- Oxidase positive
- Antibiotic resistant to penicillin, ampicillin, amoxicillin

Which microbe causes a positive hockey puck test?

Moraxella catarrhalis

HSV characteristics (3)
- Linear
- dsDNA
- Enveloped
Incubation for HSV
2-11 days

Herpes simplex virus is spread via _____
Contaminated secretions on mucous membranes
(incubation is 2-11 days. Most infectious during early days of primary infection)
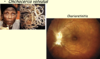
Ocular herpes definition
HSV infection of the conjunctiva w/swollen eyelids
(If the cornea is involved it is herpes simplex keratitis)
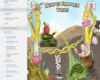
Herpes simplex keratitis (aka Dendritic Keratitis) deadens _______ and forms a _____ pattern
- nerves
- Virus branches out in the dendritic pattern


Dendritic keratitis AKA herpes simplex keratitis

Adenovirus characteristics
- Non-enveloped
- Icosahedral
- Double-stranded DNA

Cytomegalovirus characteristics (2)
- Double-stranded DNA
- Membrane enveloped
(Latency and reactivation; related to HSV)

Adenovirus transmitted by _____ (2).
- Direct contact
- Fecal-oral
(occoasionally water-borne)
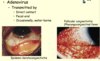
CMV retinitis: symptoms (3)
- floaters
- flashes
- blind spots
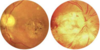
Define Pizza Pie retinopathy is caused by ______(virus) and presents with _______(3).
- caused by CMV
- Wool spots
- Infiltrate
- Hemorrhaging

Retinopathies caused by CMV are prevelent in which patient population?
- Immuno-compromised
- Neonates of mothers who are infected

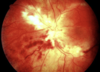
pizza pie retinopathy
(CMV virus)

Wart like lesions of the eyelides can form from the _____.
pox virus (VZV)
Sabouraud dextrose agar is used almost exclusively for ______.
fungal species

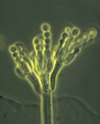
Most commonly seen fungi in the lab?

Aspergillus

What are the top 2 most commonly recovered fungi in opportunistic mycoses?
- Candida
- Aspergillus
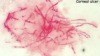
Aspergillus, but you can’t determine the exact fungi. still gives you a direction for trmt

Acremonium: 3 species that cause infection
- •Acremonium falciforme
- •Acremonium kiliense
- •Acremonium recifei
Acremonium morphology
Conidia usually appears in clusters or balls