For Exam 3 Flashcards
(228 cards)
What are 5 major functions of stems?
- Conduct water and minerals from root to leaves.
- Conduct nutrients and photosynthates (foods) from leaves to flowers and roots
- Provide aerial support
- Some modified for storage
- Some photosynthetic (ex. cactus)
Name 3 characteristics of Herbaceous stems and give examples of Monocots and Dicots for these.
- Green
- Fleshy
- Flexible
Monocots: most grasses, lilies, some orchids Dicots: Beans, mint, parsley, daisies
Name 4 characteristics of Woody stems. Give examples of Monocots and Dicots for these.
- Typically not photosynthetic
- Hard
- Inflexible
- May be adapted for gas exchange
Monocots: bamboo, palm
Dicots: apple, oak, hickory, birch, maple, magnolia
Name a & b

a. terminal bud
b. axillary bud
Name c & d

c. node
d. internode
Name e & f

e. lenticel
f. terminal bud scale scars
Name g & h

g. bundle scar
h. leaf scar
Compare the Vascular tissue arrangement for Monocot and Dicot stems.
Monocot: scattered
Dicot: ring
Compare the presence of pith in Monocot and Dicot stems.
Monocot: no pith
Dicot: has pith
Compare the presence of Cortex cells in Monocot and Dicot stems.
Monocot: has some (depends on species)
Dicot: has cortex cells
Name e

e. Epidermis
Name a, b & f

a. cholenchyma
b. parenchyma
f. cortex
Name g, h & i

g. phloem
h. vascular cambium
i. xylem
Name c

c. vascular bundle
Name d

d. pith
Name a

a. epidermis
Name b

b. parenchyma
conjunctive: filling in the spaces
no pith
no vascular cambium
no secondary growth
Name c

c. xylem
Name d
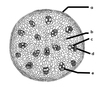
d. phloem
Name e

e. vascular bundles
What 3 things are produced during primary growth?
- Primary xylem
- Primary phloem
- the first vascular cambium cells
What is Secondary xylem and secondary phloem?
Xylem and phloem tissue produced as a result of vascular cambium activity.
Are primary xylem and primary phloem still present after secondary growth occurs?
yes
Describe the development of secondary xylem and secondary phloem in 3 steps.
- Vascular cambium cells divide and produce cells that become immature xylem and phloem cells, adding to the existing sylem and phloem tissue.
- Immature cells differentiate into their functional cell types.
- End result is an increase in xylem and phloem tissue volume. Vascular cambium cells will continue to divide to produce more cells to the inside (xylem) and outside (phloem).























































