Genetics Flashcards
(27 cards)
Cytoplasmic Inheritance
Drug resistance in many microorganisms is regulated by cytoplasmic DNA, known as plasmids, that contain one or more genes. Plasmids can be passed from one bacterial cell to another via transformation.
Nondisjunction
Is either the failure of homologous chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis I or the failure of sister chromatids to separate properly during meiosis II.
Zygote
A zygote is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote’s genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information necessary to form a new individual.
Trisomy
- The resulting zygote might either have three copies of that chromosome called trisomy(somatic cells will have 2N+1 chromosome.)
- Nondisjunction
- ex. down syndrome,
- Nondisjunction can also happen in sex chromosome.
- ex. Klineffeller syndrome.( extra copy of X chromsome) XXY or XYY
Monosomy
The resulting zygote will have a single copy of that chromosome called monosomy(somatic cells will have 2n-1 chromosomes).
Nondisjunction can also happen in sex chromosome.
ex. Turner syndrome. there is no second copy of the sex chromosome. XO. they are not fertile.
Sickle Cell Anemia
substitution of Valine for glutamic acid. this is a single base pair substitution .
Bacterial Genome
Bacterial Genome consist of a single circular chromosome located in the nucleoid region of the cell.it also has a circular rings of DNA called plasmids, which contain acessory genes.
Episomes
are plasmids that are capable of integration into the bacterial genome.
How do bacterial increase Genetic Variance
the three mechanism for increasing genetic variance of a population in bacteria
- Transformation
- Conjugation
- Transduction
Bacterial cells reproduce through binary fission which is an asexual process.
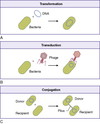
Transformation
Is the process by which a foreign chromosome fragment (plasmid) is incorporated into the bacterial chromosome via recombination, creating new inheritable genetic combinations.
Conjugation
Conjugation can be described as sexual mating in bacteria; it is the transfer of genetic material between two bacteria that are temporarily joined.
Only bacterials with plasmid called sex factors( F factors) F+ can conjugate.
Genetic material is transferred from the F+ to the F-.
These are Hfr cell

Transduction
Transduction is the process by which foreign DNA is introduced into a bacterial cell by a virus or viral vector.
Transduction happens through either the lytic cycle or the lysogenic cycle. If the lysogenic cycle is adopted, the phage chromosome is integrated (by covalent bonds) into the bacterial chromosome, where it can stay dormant for thousands of generations.
If the lysogen is induced (by UV light for example), the phage genome is excised from the bacterial chromosome and initiates the lytic cycle, which culminates in lysis of the cell and the release of phage particles.
The lytic cycle leads to the production of new phage particles which are released by lysis of the host.
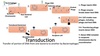
A bacteriophage
is a virus that infects its host bacterium by attaching to the bacterium, boring a hole through the bacterial cell wall and injecting its viral DNA while its protein coat remains attached to the cell wall.
Recombination
occurs when linked genes are separated. It occurs by breakage and rearrangement of adjacent regions of DNA when organisms carrying different genes or alleles for the same traits are crossed.
The operator
is the sequence of nontranscribable DNA that is the repressor binding site.
RNA polymerase must move past the operator to transcribe the structural gene.
The promoter
Is the noncodng sequence of DNA that serve as the initial binding site for RNA polymerase.
Regulator gene
it codes for the synthesis of a repressor molecule that binds to the operator and blocks RNA polymerase from transcribing the structural genes.
Inducible systems
require the presence of a substance called an inducer, for transcription to occur.
In an inducible system, The repressor binds to the operator, forming a barrier that prevents RNA polymerase from transcribing the structural gene.
For transcription to occur an inducer must bind to the repressor, forming an inducer-repressor complex. This complex cannot bind to the operator thus removing it as a barrier and permitting transcription which produce an enzyme.
The inducer is the substrate and when it is present enzymes are synthesized.
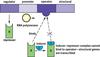
repressible systems
Repressible systems are in a constant state of transcription unless a corepressor is present to inhibit transcription.
The repressor is inactive until it combines with the corepressor(which is often the end product). The repressor can bind to the operator and prevent transcription only when it has formed a repressor- corepressor complex.
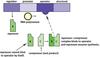
Autosomal Dominant
A pattern of inheritance in which an affected individual has one copy of a mutant gene and one normal gene on a pair of autosomal chromosomes.
-Affected parents can have unaffected children. Don’t skip generations.
Autosomal: Not sex-linked
HH= severe disorder (homozygous dominant)
Hh= disorder (Heterozygous)
hh=healthy (homozygous recessive)
ex. Huntington’s disease,
Autosomal recessive
Autosomal recessive diseases require that the individual have two copies of the mutant gene.
Skips a Generation. Unaffected parents can have affected children.
ex. sickle cell(chromosome 11), cystic fibrosis(chromosome 7),PKU(chromosome 12), Albinism
(H) healthy= Dominant
(h) disorder= Recessive
HH= healthy individual (homozygous Dominant )
Hh= Healthy(carrier) [Heterozygous )
hh= disorder. (homozygous recessive)
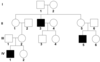
Autosomal Recessive Pedigree
- affect equal number of men and women.
- can skip a generation due to dominant- phenotype carriers.
- Autosomal recessive patterns are most clearly identified when two unaffected individuals have an offspring that are affected, which can only result from a recessive trait.

Note: that the presence of skipping definitvely indicates a recessive trait, but the absence of skipping does not necessarily indicates dominance.
Autosomal Dominant Pedigree
Appear in every generation.
Affect equal number of males and females.
Only homozygous recessive are unaffected.
Inoder to prove an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance, there must be two affected individuals who have an unaffected offspring.
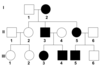
X-linked recessive Pedigree
- When a trait is X-linked recessive a person will be affected if he or she possess only the affected X chromosomes.
- Males can inherit it from their mother only.Thus affected mom or carriers can pass these traits on their sons.
- Since males can’t be carriers( Only affected or unaffected), females who inherit these traits must have a father who is affected and a mother who is either a carrier or affected.
- ex. color-blindness and hemophilia.
- Skip a generation.
- If significantly more males are affected than females and two unaffected individuals produce an affected offspring, then a trait is likely X-linked recessive.