reproductive system and development Flashcards
(16 cards)
upon ovulation, the oocyte is released into the
Abdominal cavity.it is then drawn to the Fallopian tube by cilia. It is fertilized in the Fallopian tube.
The male reproductive
Prostate. Bulbourethral Cowper’s Seminal vesicles
spermatogenesis( maturation of sperm)
spermatogonia(2N)→primary spermatocyte(2N)→secondary spermatocyte(N)→spermatid(N)→spermatazoa
Ovulation is directly caused by
Ovulation occurs when the Luteinizing hormone (LH) spikes in response to sharp increase in follicle-stimulating hormone(FSH), which in turn was caused by rising estrogen levels from the developing follicle. LH causes the follicle to rupture, releasing its ovum, and this is ovulation. The follicle leaves behind the corpus luteum, which is what gives LH its name.
1.Organogenesis
final stages of development
The body organs begin to form. In this process, the cells interact, differentiate, change physical shape, proliferate and migrate.
2.Growth
final stages of development
The organs increase in size, which is a continual process from infancy through childhood to adulthood.
3.Gametogenesis
final stages of development
Eggs develop in women and sperm develop in men, which permits reproduction to occur.
Congenital Disorder
are birth effects that are caused by teratogens including drugs, alcohol, tobacco virus etc.
When a mother passes on an infection directly to her developing offspring it is called a vertical transmission.
Epicotyl
Cotyledons
The precursor of the upper stem and leaves
Seed leaves.
dicots have two seed leaves, while monocots have only one .

Hypocotyl
Endosperm
The lower stem and root
Feeds the embryo in angiosperms; in dicots, the cotyledon absorbsthe endosperm.
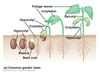
Seed coat
Develops from the outer covering of the ovule; the embryo and its seed coat together compromise the seed.

Plant development
Growth in higher plants is restricted to the embryonic(undifferentiated) cells called meristem cells.
Apical meristem
The apical meristem is found in the tips of roots and stems. Growth in length occurs only at these points.
Lateral meristem or cambium
The lateral meristem or cambium is located between the xylem and phloem. This tissue permits growth in diameter and can differentiate into new xylem and phloem cells.
It is not an active tissue in monocots(grasses) or herbaceous dicots(alfalfa) but is predominant in woody dicots like oaks.
Cleavage
It leads to an increase in cell number without a corresponding growth in cell protoplasm.
Which if the following developmental stage has the greatest nuclear-to-cytoplasmic material ratio?
Blastula


