GI Infections Flashcards
(258 cards)
What are main issues that are contributed to antibiotic resistance?
- Underdosing or not completing courses
- Use with livestock
- Selling them over the counter in some european countries
- Possibly using the prophylactically before surgery
- Releasing large quantities of antibiotics into the environment during pharmaceutical manufacturing
What is the definition of antimicrobial resistance (AMR)?
Implies that an antimicrobial will not inhibit bacterial growth at clinically achievable concentrations
What is the definition of antimicrobial susceptibility?
Implies that an antimicrobial will inhibit bacterial growth at clinically achievable concentrations
What is the laboratory effect of resistance?
If resistant in the lab, will more often than not translate into clinical environments
What is MDR?
Multidrug resistance: non-susceptibility to at least 1 agent in 3 or more antimicrobial categories
What is XDR?
Extensively-Drug resistant: non-susceptibility to at least 1 agent in all but 2 or fewer antimicrobial categories
What is PDR?
PanDrug resistance: non-susceptibility to all agents in all antimicrobial categories (no agents can fight the buggers)
What are the 2 types of resistance?
Innate or acquired (majority)
What are the 6 main mechanism of resistance?
1) Inactivation
2) Impermeability
3) Efflux
4) By-pass
5) Pbps • Penicilan binding proteins which change the structure, so that there isn’t a perfect lock of the antibiotics to the microbe
6) Altered target
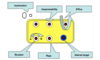
What are the 3 mechanisms by which bacteria can transfer the resistant genes?
- Bacterial transformation (direct uptake)
- Bacterial transduction (via a virus)
- Bacterial conjugation (through mating)
What are the 4 main solutions to reducing AMR?
- Preventing infections and preventing spread of disease
- Tracking these resistant bugs
- Improving antibiotic prescribing and use, aka stewardship
- Developing new drugs
What is antimicrobial stewardship?
The optimal selection, dosage, and duration of antimicrobial treatment that results in the best clinical outcome for the treatment or prevention of infection, with minimal toxicity to the patient and minimal impact on subsequent resistance
What are the 4 D’s of antimicrobial stewardship?
Dose, Duration, Drug and De-escalation
In terms of prescribing, what things must be addressed to reduce resistance?
- Broad spectrum antibiotic therapy (choose combination of narrow spectrum instead)
- Long duration of therapy (give for as short as possible)
- Low or suboptimal dose of antibiotic
- Route of therapy makes no difference IV vs Oral)
- Total amount of antibiotic use
- Giving antibiotic in the absence of infection
What are host factors that increase risk of GI infections?
- Age (very young & elderly)
- ↓ gastric acid secretion
- ↓ gut motility
- Influence of colonic microflora
- Altered intestinal immunity
What is the definition of diarrhoea?
3 or more loose stools in 24 hours
What kind of bacteria is campylobacter (c. jejuni or c. coli)?
Gram negative bacillus
What is the incubation period of campylobacter?
3-10 days
What is the commonest cause of bacterial GI infection in the UK?
Campylobacter
What is the mechanism of action of campylobacter?
Causes inflammation of colon and rectum→bloody diarrhoea
What is the source/vehicle of infection of campylobacter?
Farm animals - especially undercooked poultry, but also water and unpasteurised milk
What is the management of unresolved campylobacter with systemic illness?
Erythromycin or ciprafloxin for 5 days
What is the incubation period of salmonella enterica?
Medium - 12-48hrs
What is the mechanism of action of salmonella enterica?
Causes inflammation of ileum and colon – cause mucosal damage, ↓fluid absorption and ↑fluid excretion • Which is what causes the loose stools and diarrhoea




