H&N week 9- maxillary nerve, nasal cavity. Flashcards
(40 cards)
What are the nares?
The nares are the nostrils.
What do we call the posterior nares
The choanae
Discuss the lining of the nasal cavity.
The Nasal cavity is lined with respiratory epihthelium.
This is pseudostratifed columnar cells with cilia and goblet cells dispersed between them.
The nasal septum has olfactory epithelium on it.
What is the lateral nasal cartilage.
The lateral nasal cartilage is an extention of the septal cartilage which gives shape to the nose.
Discuss the function of the nose and how it works.
The nose warms and cleans air.
The high blood supply to the mucosa warms the air.
Mucosus sticks to the dust being inhaled.
The Cilia waft the mucous back into the nasopharynx to get rid of it.
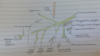
Label this diagram of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity

Discuss the concha
Concha are large folds of bone covered by mucosal membrane that project into the nasal cavity from the lateral wall.
There are 3 concha:
Inferior-
Middle- A fold of bone above the inferior concha which is slightly smaller and at a bit of an angle.
Superior- A little peice of bone which is quite often fused with the middle concha at the front end.

What are the meatuses?
The Meatus is the space underneath the concha where air passes through.
We name the meatus after the concha located above it.
There is:
The inferior meatus
The middle meatus
Superior meatus.

What is the spheno-ethmoidal recess?
The area above the superior concha between the sphenoid bone and the ethmoid bone.
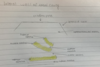
Label this diagram of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity with the concha removed


What is the frontal air sinus?
An air containing space found inside the frontal bone, there is one found on each side of the nose.
Where does the frontal air sinus open?
At the top end of the hiatus semilunaris.
What is the nasolacrimal duct?
A duct that is draining tears into the nasolacrimal sack.
The opening is on the lateral wall of the nasal cavity into the inferior meatus
What is the hiatus semi-lunaris?
A crescent moon shaped recess in the middle meatus.
What is the ethmodial bulla?
A bulging peice of bone covered by mucous membrane in the middle meatus. The bone contains lots of air cavities.
Why is it common for patients’ with frontal sinusitis to also have maxillary sinusitis?
because the sinus openings are located so close to each other it is easy for the bacteria to drop from one sinus to another.
What are the sphenoidal sinuses?
Air pockets that sit right below the sphenoid bone and are lined with respiratory epithelium.
Where does the pituitary gland sit?
In the sella turcica.
Where do the sphenoidal sinuses open?
Into the spheno-ethmoidal recess.
label this diagram of the maxillary sinus


What is the maxillary sinus?
An air cavity within the maxillary bone.
This makes the bone lighter and gives it strength.
The maxillary sinus is lined by respiratory epithelium.
Discuss the opening of the maxillary sinus?
This opens at the inferior end of the hiatus semi-lunaris.
But this is at the top of the sinus- which makes it much more difficult to drain.
Cilia are more plentiful at the opening of the maxillary sinus.
What are the ethmoidal sinuses?
Lots of little air spaces found in the ethmoid bone.
Discuss the floor of the orbit?
The orbit floor acts as the roof of the maxillary sinus.
But the orbital floor is thin & weak so can break.