Lecture 4&6: Lymphoid Tissue I & II Flashcards
(100 cards)
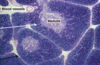
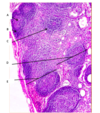
What is the arrow pointing at and where would you find this tissue?

Arrow is pointing at CT and this is GI tissue
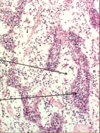
What is the arrow pointing at and where would you find this tissue?

The airway is pointing at CT and this is airway tissue
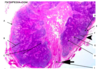
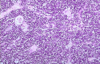
What is this a picture of?

Primary nodule (singular nodular tissue - non-encapsulated lymphoid tissue)
- Far more infrequent than secondary nodules
- Consist of only small lymphocytes
- Prenatal
- do not possess a germinal center
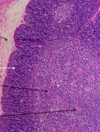
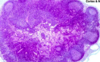
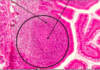
What is the circle and the 2 arrows in this picture?

Circle = secondary lymphoid nodule (singular nodular tissue, non-encapsulated lymphoid tissue)
Left arrow = mantle zone
Right arrow = germinal center
What is this a picture of?

Secondary lymph nodule
What is this a picture of?

Primary lymph nodule
Name the 3 tonsils in the picture

Top = pharyngeal tonsil (adenoids)
Middle = palatine tonsils
Bottom = lingual tonsils

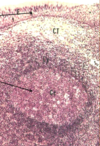
What type of tonsil is this and what are the 2 arrows indicating?

Pharyngeal tonsil
Top arrow = pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
Bottom arrow = germinal center
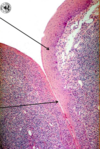
What type of tonsil is this and what are the arrows indicating?

Palatine tonsil
Top arrow = stratified squamous epithelium
next = partial capsule
Next = germinal centers
Bottom = crypts

What is this a picture of and what do the arrows indicate?
Lingual tonsil
Top arrow = stratified squamous epithelium
Bottom arrow = one crypt per tonsil
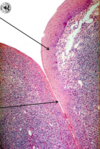
What is this a picture of?

Palantine tonsil
What is this a picture of?

Lingual tonsil
What is this a picture of?

Pharyngeal tonsil
What do the arrows in this picture indicate?

Left = ileum
Middle = villi
Right = lymphoid tissue

What does the box in this picture indicate?

GALT -> AKA Peyers patches
Where is this tissue found?
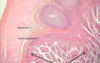
Small intestine
Where is this tissue found?

Vermiform appendix
Where is MALT found?
GI tract, respiratory passageways and urinary tract
GALT is called Peyers patches in the ileum and is characterized by an abundance of ______
Villi
GALT in the vermiform appendix is characterized by crypts and no ______
villi
How many palatine tonsils does a person have
2
How many pharyngeal tonsils does a person have
1
How many lingual tonsils does a person have?
Small and numerous
Where are palatine tonsils found?
Lateral walls of oral cavity