Lecture 4.5: V/Q ratio Flashcards
(8 cards)
If A-a gradient is normal but the PaO2 and the PAO2 are low, then what can you infer about the pathology?
That it is NOT in the alveoli
Describe what is being picture in this graph
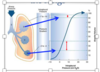
Shows that the intraplueral pressure of the apex is higher than the base, because of the locatios relative to the heart
Also shows that the base alveoli are able to expand more becuase they have smaller alveoli and more room to expand than in the apex of the lung
Describe what happens in the event of a low V/Q ratio
The oxygen is not getting to the alveoli as much or at all, but the blood is still coming into the area
The alveolar gasses start to drop because the oxygen that it is exchanging with the blood is not replinished
Over time, the alveolus equilibrates with the non-arterialized blood
Right to left shunt occurs
In teh event of a change in the VQ ratio, what does the body do in an attempt to maintain homoestasis
Want hypoxic vasoconstriction, so that the blood stops going to the alveoli that are not able to make any significant changes
Describe what is happening physiologically in a high V/Q ratio
No blood is being delivered to the alveoli
dead space
alveoli start to match the atmospheric air and have a shit ton of oxygen BUT the body does not benefit from this because there is no blood coming here
BUT the same amount of blood is still going to the lungs so that alveoli that DO get blood flow get double the blood and are not able to keep up with the gas exchange
start to look like the venous blood and act like a low V/Q
Describe the apex of the lung in terms of
- blood flow
- areolar ventilation
- V/Q ratio
- PaO2
- PaCO2
- Lowest blood flow
- Lower alveolar ventilation (because theyre big boiz)
- High V/Q ratio
- Highest PaO2
- Lower PaCO2
Describe the base of the lung in terms of
- blood flow
- areolar ventilation
- V/Q ratio
- PaO2
- PaCO2
- highest blood flow
- higher alveolar ventilation
- lower V/Q ratio
- lowest PaO2
- higher PaCO2
Describe and account for any differences in the pH of the apex and the base of the lungs
The apex has a low PaCO2, meaning that is is less acidic, so the pH in the alveoli is higher and more basic
The base has a high PaCO2 and is more acidic so the pH is lower


