MCP Flashcards
(32 cards)
name structure

amylopectin
name structure

amylose
name structure

cellulose
name structure

galactose
name structure

fructose
name structure

glucose
name structure

glycogen
name structure

isomaltose
name structure

lactose
name structure

maltose
name structure
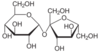
sucrose
name linkage
alpha linkage
name linkage
beta linkage (draw beta going up)
(L/D) sugars are more abundant biological structures
D
four major dietary carbs
amylose (starch, amylopectin (starch), lactose, sucrose (table sugar)
why can we not digest cellulose
we dont’ have an enzyme that cleaves a beta 1-4 linkage
where is table sugar digested
in the small intestine by brush border enzymes
where does starch digestion begin
in the mouth, with amylase
increased levels of serum amylase probably indicates
pancreatitis
the specificity of glycosidases is based on these three things
type of linkage, type of sugars, position of the linkage (terminal or internal)
(starch/disaccharides) are cleaved in the mouth by salivary amylase
starch
difference between lactase non persistence and lactose intolerance
lactase non persistence–enzyme is no longer expressed at high levels
lactose intolerance–symptoms
NADPH is critical for (synthesis/degradation) pathways
synthesis
gluconeogenesis makes glycogen from (monosaccharides/amino acids)
amino acids, lactate


