Midterm I - Miscellaneous Photos & Info Flashcards
(220 cards)

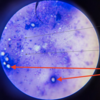
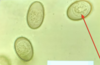
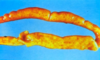
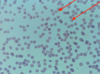
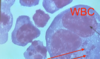
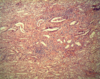
Trypanosoma sp.: Trypomastigotes
Blood smear

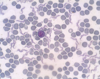
Trypanosoma equiperdum: Trypomastigotes

Trypomastigote in the blood

Trypanosoma sp.: Trypomastigote
Fish blood
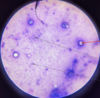
Leishmania sp.: Promastigotes

- Leishmania sp.*: Promastigotes
- Extracellular forms*
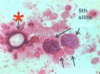
Leishmania sp.: Amastigotes
Divided & intracellular - Only in macrophages
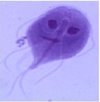
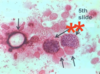
Giardia sp.: Trophozoite
Containing 2 nuclei

Giardia sp.: Trophozoites
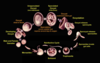
AfricanTrypanosoma sp.: life cycle

Trypanosoma sp.: Form type in the vertebrate host tissue
Amastigotes

Trypanosoma sp.: Form type(s) in insects
- Promastigote
- Epimastigote

Trypanosoma sp.: Form type in the vertebrate host’s blood
Trypomastigote
“Metacyclic form”
Trypanosoma sp.: Symptoms
- Genital & abdominal oedema
- Cachexia
African Trypanosoma sp. “Salivaria”: Vector
Tsetse fly
Males & females
Trypanosoma equiperdum: Life cycle

Trypanosoma cruzi: Life cycle

Leishmania sp.: Life cycle
Passed on by the saliva (not faeces)

Leishmania sp.: Form type In vertebrates
Amastigotes
Leishmania sp.: Form type In insects
Promastigotes
Leishmania sp.: Vector
Female sand fly
Leishmania tropica: Pathological form
Cutaneous form (skin)
Leishmania braziliensis: Pathological form
Mucocutaneous form (oral & nasal cavity)
Leishmania donovani: Pathological form
Visceral form (liver, spleen etc.)