Nervous System - Spinal Cord Flashcards
(33 cards)
1
Q
Gray Matter
A
- shaped like a butterfly
- primary contains neuronal cell bodies (nuclei)
- contains ventral and dorsal horns
- lateral horns located in thoracic and sacral section of the spinal cord
2
Q
Lateral Horns
A
- part of gray matter in spinal cord only located in the thoracic and sacral regions of the spinal cord
3
Q
White Matter
A
- surrounds gray matter in the spinal cord
- primarily contains neuron axons (tracts)
4
Q
Nuclei
A
- cell bodies in the CNS
- gray matter in the spinal cord
5
Q
Tracts
A
- axons in the CNS
- located primarily in the white matter
6
Q
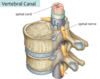
Vertebral Canal
A
- the channel through the center of the vertebral column
- formed by successful vertebral foramina“stacked” on top of one another
7
Q
Sacrum
A
- sacral region of the vertebral column
- five sacral vertebrae fused to form the sacrum
8
Q
Coccyx
A
- the inferior structure of the vetebral column
- formed by the fusion of 3-4 coccygeal vertebrae
9
Q
Intervertebral Disc
A
- the joint between two vertebral bodies - a symphysis (two bones connected by cartilage)
- the symphysis that connects the vertebrae in the spinal column
Outer Layer - Anulus Fibrosis (fibrocartilage)
Inner Layer - Nucleus Pulposis (gelatinous core)
- act as shock absorbers and allow movement of the vertebral column

10
Q
Anulus Fibrosis
A
- the other layer of the intervertebral disc
- made of fibrocartilage
11
Q
Nucleus Pulposis
A
- the inner core of the intervertebral disc
- gelatenous
- slips past the anulus fibrosis when one has a slipped disc
12
Q
Intervertebral Foramina
A
- openings on the lateral aspect of the vertebral column that permits passage of vessels and nerves into or out of the vertebral canal
- formed by superior and inferior vertebral notches of the adjacent vertebrae

13
Q
Vertebral Foramina
A
- the space located within the vertebra where the spinal cord passes through

14
Q
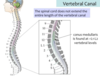
Conus Medullaris
A
- the terminal (most inferior) part of the spinal cord
- located at approximately the L2 vertebral level in adults (and as far as L3 in infants)
15
Q
Location of an LP or spinal tap
A
Between L3 and L5 so as to access CNS but not hit the spinal cord (which ends at L2 at the conus medullaris)
16
Q
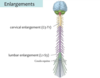
Spinal Cord Enlargements
A
- two swellings in the spinal cord
- reflect the large number of neurons pressent in those areas (generally that innervate the limbs/extremities
- Cervical and Lumbar
17
Q
Cervical Enlargement
A
- found bw C5-T1
- neruons found here innervate the upper extremities
18
Q
Lumbar Enlargement
A
- found bw L1-S3
- neruons here innervate the lower extremity
19
Q
Meninges
A
- the layers of connective tissue that surround the brain and spinal cord

20
Q
Dura Mater
A
- the thick outermost layer of the meninges
21
Q
Arachnoid Mater
A
- the middle layer of the meninges that resembles a spider web
- lies up against the dura mater

22
Q
Pia Mater
A
- the innermost layer of the meninges
- intimately applied to the spinal cord
- the most delicate membrane enclosing the brain and spinal cord

23
Q
Epidural Space
A
- aka extradural space
- the area between the dura mater and the vertebral canal
- filled with fat and also contains the internal vertebral venous plexus
- begins at the foramen magnum and ends inferiorly at the sacral hiatus
- often local anasthesia injected in order to anesthetize the nerve roots (i.e. epidural)

24
Q
Dural Sac
A
- aka thecal sac
- a tube/sac formed by the dura mater around the spinal cord
- sac begins at the foramen magnum where it is continuous with the dura mater around the brain
- extends approximately to the S2 vertebral level (varies bw S1-S3) –> continuous with the outer part of the external filum terminale (coccygeal ligament)
- has sleeve-like projections that surround the spinal nerve roots as they exit the vertebral canal

25
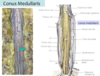
**Internal Filum Terminale**
- a thin strand of pia mater that continues inferiorly passed the conus medullaris
- becomes invested in the dura mater at the inferior limit of the dural sac
26
**External Filum Terminale**
- at the end of the dural sac where the internal filum terminale becomes invested in the dura mater
- essentially the pia mater + dura mater
- aka **coccygeal ligament**
- anchors the spinal cord inferiorly by passing through the sacral hiatus and attaching to the coccyz

27
**Subdural Space**
- potential space between the dural mater and the arachnoid mater

28
**Subarachnoid Space**
- located bw the arachnoid mater and the pia mater
- contains CSF (cerebrospinal fluid)
- extends to the end of the dural sac (S2) thus allowing CSF to be sampled without puncturing the spinal cord
- continuous with the subarachnoid space of the brain

29
**Denticulate Ligaments**
- lateral tooth-shaped extensios of the _pia mater_ that penetrate the arachnoid and fuse to the dura mater to help anchor the spinal cord within the vertebral canal

30


31


32
**Vertebral Column**
- 33 stacked vertebrae
7 Cervical
12 Thoracic
5 Lumbar
5 Sacral
4 Coccygeal

33
Fill in the meninges




