Thorax I - Thoracic Wall Flashcards
(32 cards)
Sternoclavicular Joint
- medial end of the clavicle
Acromioclavicular Joint
- lateral end of the clavicle
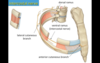
Clavicle
- bone of the pectoral girdle; superficially located
Articulates with:
- Sternum (at sternoclavicular joint)
- Scapula (at acromioclavicular joint)
Landmark:
- Midclavicular Line
Midclavicular Line
- line on the sagittal plane that intersects the midpoint of the clavicle
Sternum
- flat bone that forms part of the anterior chest wall; component of the ribcage
Three parts (superior –> inferior):
Manubrium
(Sternal Angle)
Sternal Body
Xiphoid Process
Sternal Angle
- groove that marks the articulation between the manubrium and the body of the sternum
- at the articulation of the 2nd costal cartilage with the sternum
- aka Sternal Angle of Louis or Manubriosternal Junction
Manubrium
- superior part of the sternum
Body
- middle section of the sternum
Xiphoid Process
- small peice of bone at the inferior part of the sternal body
Jugular Notch
- notch on the superior aspect of the manubrium
- aka Suprasternal Notch
Costal Margins
- the inferomedial edge of the ribcage, specifically the cartilagionous portion that connects ribs 7-10 to the sternum
Coracoid Process
- landmark on the scapula
- projects anteriorly and serves as a site of muscle attachment
Thoracic Cage
Formed by:
- 12 pairs of ribs
- 12 thoracic vertebrae
- sternum
Ribs
- flat C-shaped bones that form part of the thoracic cage
- 21 pairs
- 1-7 articulate with the sternum via costal cartilage (true ribs)
- 8-10 articulate with the cartilage of the costal margin (false ribs)
11-12 do not have an anterior articulations (false ribs, floating ribs)
True Ribs
- Ribs 1-7 that articulate with the sternum via costal cartilage
False Ribs
- Ribs 8-12 that do not articulate with the sternum
- 8-10 articulate with the cartilage of the costal margin
- 11-12 do not have articular articulation = Floating Ribs
Floating Ribs
- ribs 11-12 that do not articulate anteriorly with the sternum or the cartilage of the costal margin
Thoracic Cavity
- area within the thoracic cage
- separated from the abdominal cavity by the diaphram
Superior Portion of the Abdominal Cavity
- located inferiorly to the thoracic cavity
- contained within the thoracic cage
Contains:
- liver, spleen, pancrease, stomach
Intercostal Spaces
- lie between adjacent ribs
- how gain access to the thoracic cavity
Contains:
- intercostal muscles (3 layers)
- intercostal arteries, veins, and nerves
Intercostal Muscles
- fill gaps between adjacent ribs
- move ribs, thought to assist inspiration/experation
3 Layers:
External Intercostal (most superficial)
Internal Intercostal
Innermost Intercostal (most deep) - also includes transversus thoracis muscle
- intercostal nerve, arteries, and veins located between the internal and innermost muscle layers
Intercostal Arteries
- travel with the intercostal nerves
- anterior and posterior intercostal arteries can develop anastomotic connections providing collateral channel if aorta or internal thoracic artery becomes occluded
VAN - order from superior to inferior
1 - Veins
2 - Arteries
3 - Nerve
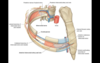
Posterior Intercostal Arteries
- branches of the thoracic aorta
Anterior Intercostal Arteries
- branches of the internal thoracic artery