Nose and Throat Flashcards
(15 cards)
What are the differentials for a neck lump in the posterior triangle?
Cystic hygroma - congenital
Cervical rib - thoracic outlet syndrome
Pharyngeal pouch - halitosis, retrosternal discomfort, dysphagia
Subclavian aneurysm
Lymph nodes
What are the differentials for a neck lump in the anterior triangle?
- Branchial cyst - painless, firm swelling.
- Carotid body tumour (chemodectoma)
- Carotid artery aneurysm - pulsatile
- Salivary gland
- Laryngocele
What are the differentials for a midline neck lump?
- Thyroid goitre
- Thyroglossal cyst
- Thyroid cyst
- Carcinoma
- Lipoma
- Dermoid cyst
- Epidermal cyst
- Abscess
- Lymphoma
What is a cystic hygroma and what is it associated with?
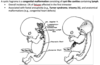
What are the clinical features of a cystic hygroma?
Clinical features:
- Soft, compressible, painless neck mass
- Classically found in the posterior triangle of the neck
- Can cause dysphagia or airway compromise
- Can be transilluminated
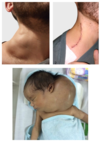
Describe the diagnosis and management of a cystic hygroma
Diagnosis is usually at prenatal ultrasound: fluid-filled structure that can be single or multilocular.
CT or MRI may be used to further assess anatomical structures for surgical planning.
Treatment: Small masses may regress spontaneously, but surgical excision is indicated to prevent infection of the mass or airway compromise.
Talk to me about a cervical rib
A cervical rib is an extra rib that forms above the first rib, growing from the base of the neck just above the collarbone. It can be bilateral or unilateral.
Cervical ribs can cause thoracic outlet syndrome (Thoracic Outlet Syndrome) which can present with:
- Arterial compression (arm fatigue, ache, Raynaud’s, 6Ps)
- Venous compression (swelling, heaviness)
- Nerve compression (paraesthesia, pain).
Can be managed with surgical removal of cervical rib.
What is a pharyngeal pouch and it’s epidemiology?
A pharyngeal pouch is a type of oesophageal diverticulum (Zenker diverticulum). That occur in middle-aged to older patients.
Describe the clinical presentation and diagnosis of a pharyngeal pouch
Clinical presentation depends on diverticulum size and localization:
- Dysphagia (most common)
- Halitosis (exam clue)
- Regurgitation of undigested food
- Aspiration
- Coughing after food intake
- Retrosternal pressure sensation and pain
Best diagnosed on barium swallow and can be managed surgically.
What is a branchial cyst?
A Branchial cyst is a remnant of the embryological second branchial cleft or cervical sinus.
- Accounts for 20% of paediatric neck masses
What are the clinical features and management of a branchial cyst?
Usually diagnosed in late childhood/adulthood after previously undiagnosed cyst becomes infected.
- Often a history of preceding upper respiratory infection
Otherwise presents as a painless, firm mass lateral to midline, usually anterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, which does not move with swallowing.
Treatment: complete surgical excision of both the cyst and any associated tracts
Talk to me about a caroid artery aneurysm
An external carotid artery aneurysm is caused by atherosclerosis, trauma or infection.
Presents as pulsatile lateral neck mass which doesn’t move on swallowing. There may be associated bruit. It may also have an affect on associated structures such as to cause voice hoarseness and dysphagia.
Treatment: surgical repair, either in the form of an aneurysm excision and reconstruction or endovascular repair (grafting or stenting)
What is the definition and epidemiology of Thyroglossal Cyst?
A thyroglossal cyst is a fibrous cyst that forms from a persistent thyroglossal duct.
- They are the most common cause of midline neck masses (does this doesn’t include goitres?) and are generally located below the hyoid bone.
What are the clinical features of Thyroglossal Cyst?
Present as a palpable asymptomatic midline neck mass above/below the level of the hyoid bone. The mass moves on swallowing or on protrusion of the tongue because of its attachment to the tongue.
Some patients will have neck or throat pain, or dysphagia.
The cyst can become infected after respiratory tract infection, which may cause enlargement of the cyst, aiding in diagnosis. Otherwise, up to half of cysts are not diagnosed until adulthood. The tract can lie dormant for years until some stimulus leads to cystic dilation. Spontaenous drainage can also occur.
Describe the investigations and management of a thyroglossal cyst
Investigations
Thyroid function tests should be performed to exclude a thyroid nodule. A thyroglossal cyst does not have any thyroid cells, rather it has mucoid cells.
Ultrasound and radioactive iodine or technetium scan can show the presence of a thyroglossal cyst.
Management
- Elective surgical excision (Sistrunk procedure) to prevent infection
- Treatment of any active infection with antibiotics before surgery


