Ocular Pathology Flashcards
(115 cards)
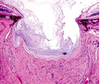
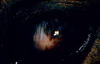
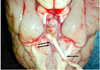
What ocular abnormality is present?

Corneal edema
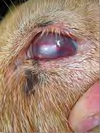
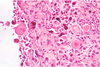
MDx

MDx: cataract
Causes of corneal opacity
Corneal edema- MOST COMMON- fluid in the corneal stroma
– Injury to epithelium (ulceration)
– Injury to endothelium
• Cornealendothelial
dystrophy
• Increased IOP (Glaucoma) • Immune-mediated
– Keratitis–neovascularization has leaky capillaries
Corneal deposits – covered later

Corneal edema due to an ulcer
Ulcer stains green with flourescein dye

Corneal edema due to keratitis
Note gross features of inflammation

MDx: diffuse corneal edema
Corneal endothelial dystrophies
Inherited; breed predilections
Old age change
Bilaterally symmetrical foci of opacity which progress to diffuse opacity
Endothelial degeneration of unknown cause
It’s a gross diagnosis! - no histo!

MDx: diffuse corneal edema
Puppy that survived the acute phase of infectious canine hepatitis (CAV-1 infection); immune complex deposition in corneal endothelium
“Blue Eye”

Cataract
The most common disease of the lens
Swelling/degeneration of lenticular fibersopacity

Lens response to injury:
Hydropic swelling of injured fibersfiber fragmentation & disintegration
Hyperplasia and fibrous metaplasia of lens epithelium
Posterior lens epithelial migration
When chronic (“hypermature”): shrinking and wrinkling of lens capsule and mineralization
What causes a cataract?
Radiation
Increased IOP (Glaucoma)
Endophthalmitis
Hereditary defect in lenticular metabolism
Diabetes mellitus (high glucose in aqueous)
Trauma
ANYTHING THAT DAMAGES THE LENTICULAR FIBERS!
What do you evaluate in a fundic exam?
Indications of retinal degeneration (& atrophy)
- Decreased vascularity
- Optic disc atrophy
- Changes in tapetal reflection
If you are loosing retina, the tapendum will become ______ reflective?
MORE
Causes of retinal degeneration & atrophy
Senile change
Inherited metabolic defect of photoreceptor cells
– Collectively known as PRAs (“progressive retinal atrophy”)
– SARD
Toxicity
Metabolic deficiencies – taurine, vitamin A
Increased IOP (glaucoma)
Retinal detachment

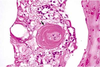
Retina from an adult cat with acquired blindness
Lost photoreceptor and outer nuclear & plexiform layers
Morphologic diagnosis: Retinal atrophy (& degeneration)
Cause:
Enrofloxacin toxicity
histo can’t tell you the etiology

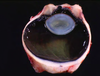
Retina from a horse with increased IOP (glaucoma)
Loss of nerve fiber and ganglion cell layers, but excellent preservation of photoreceptors and outer nuclear layer
MDx: retinal atrophy
Causes of retinal detachment (separation)
Exudative
– Choroiditis, retinitis – Hemorrhage
– Neoplasm
• Tractional
– maturation of fibrin in vitreous (fibrous adhesions between ciliary bodies = “cyclitic membrane”)
Usually due to inflammation

Retinal detachment due to effusion from the growth of metastatic lymphoma within the choroid and subretinal space
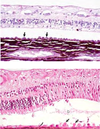
Retinal detachment (separation)
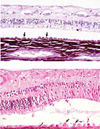
Consequence = retinal degeneration & atrophy
Separates between neural and pigmented layers
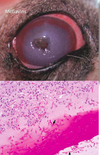
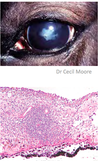
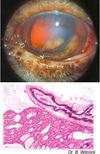
What is the most likely cause of the corneal opacity?

Glaucoma
Glaucoma
= ↑ IOP
• bad bad BAD
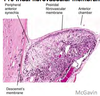
obstruction of the filtration angle
Primary Glaucoma
Cause = goniodysgenesis, a detectable malformation of the trabecular meshwork
Dogs – inherited, common
Other species – severely anomalous eyes
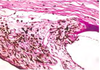
Goniodysgenesis, primary glaucoma
Secondary Glaucoma
Most common type
Causes = anything that obstructs the pupil or trabecular meshwork
– Exudate(endophthalmitis)
– Lens luxation
– Posteriorsynechia
– Peripheralanteriorsynechia
– Compression of the filtration angle