Oral path photos Flashcards
(272 cards)

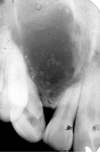
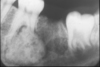
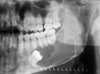
Odontogenic Myxoma
o Radiographic feature: thin septations at right angles to each other. Thin, wispy septations.
o Can grow large; resection is difficult as tumor is jelly-like and may send myxoid fingers into surrounding bone, not visible on imaging.
o Conservative resection necessary.

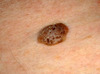
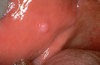
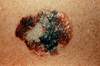
Oral Melanotic Macule
- 2:1 female predilection
- tan to brown round macule, usually solitary
- tx not required, biopsy if unknown etiology

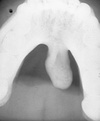
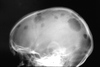
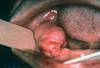
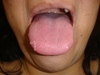
Ranula
- Mucocele on floor of mouth
- plunging = dissecting through mylohyoid. May grow large.
- DDx
- Dermoid cyst is in ddx,
- Cystic Hygroma (neck lymphangioma).

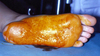
Hemangioma (Arterio-venous Malformation)
- Multilocular RL ddx (if intraosseous).
- Aspirate prior to biopsy
- Congenital hemangiomas often spontaneous resolve toward adulthood

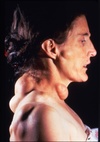
Erythema Multiforme
- Probably autoimmune; 50% pts had other infx
-
EM Minor: Target lesions of skin, assoc w/ HSV
- Mostly male, 20s-30s, self-limiting (2-6 wks)
- 20% recurrence, irreg lesions necrose/ulcer
-
EM Major: (Stevens-Johnsons Syndrome)
- Sick Patients, trigger often a med, 5M/yr
-
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)
- Old pts, tx in burn unit, sloughing of skin

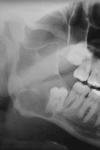
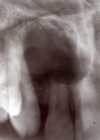
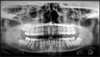
Osteosarcoma
Freq in long bones: proximal tibia/distal femur, in pubescent boys. Gnathic osteosarcs = older age, average 35. X-ray hallmarks of osteosarcoma: asymm widening of PDL space; bone formation in soft tissue; bone formation above the alveolar crest. Spiking root resorption; irregular, ill-defined borders; may be RL to Mixed to RO; “Sun-burst” only in 25% of jaw osteosarcs. Radical resection is only effective tx.

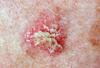
Veruccous Carcinoma
- A less aggressive, less invasive variant of conventional SCC.
- Exhibits a prominent papillary, exophytic growth pattern.
- Does not metastasize; if metastatic, likely represents transformation to conventional SCC.

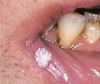
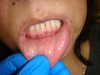
Eruption Cyst
o Overlying soft-tissue impacted tooth, may clinically appear blue or red.
o Usually, spontaneous resolution with subsequent eruption of the tooth, no need to make an incision.

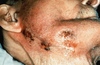
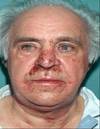
Wegeners Granulomatosus
- “Saddle Nose,” affects Respiratory/Renal Systems
- Oral Manifestation = “Strawberry Gingiva”
- before renal involvement
- florid, granular hyperplasia (bumpy, hemorrhagic, and friable)
- bone destruction and tooth mobility

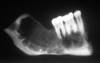
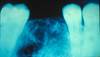
Central Giant Cell Granuloma
- Multilocular RL ddx; some may be aggressive.
- Can be associated with aneurysmal bone cyst
- Same histology seen in Cherubism; Brown Tumors of hyperparathyroidism.

Macule
- A circumscribed flat area, up to 1.0 cm in diameter
- Perceptibly different color from surrounding tissue

Papule
- A circumscribed, solid elevation in skin or mucosa

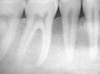
Buccal Bifurcation Cyst
Be familiar with typical clinical presentation
- associated tooth is vital
- tx with curettage
- DO NOT extract tooth.

McCune-Albright Syndrome
- Polyostotic Fibrous Dysplasia
- Cafe-au-lait (Coast of Maine)
- Endocrinopathies (early menses in Females)
- Hockey Stick deformity to Femur

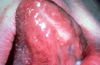
Squamous Papilloma
- HPV subtypes 6 & 11 found in 50% of squamous papillomas
- tongue, lips; most common soft tissue mass of soft palate
- cauliflower appearance, finger-like projections
- Papilloma Ddx= Squamous Papilloma, Verruca Vulgaris, Condyloma Acuminata, Heck’s Disease

HSV-1
- Cold sores…not the same as Canker sores/apthae
- Typically initially presents in Kids, crusting mouth, low fever
- Rarely initial presentation in adults, high fever, pharnyx

Erythema Multiforme
Probably autoimmune; 50% pts had other infx
EM Minor: Target lesions of skin, assoc w/ HSV
- Mostly male, 20s-30s, self-limiting (2-6 wks)
- 20% recurrence, irreg lesions necrose/ulcer
EM Major: (Stevens-Johnsons Syndrome)
- Sick Patients, trigger often a med, 5M/yr
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)
- Old pts, tx in burn unit, sloughing of skin

Osteoma
- Benign neoplasm; multiple seen in Gardner’s syndrome.
- Primarily craniofacial distribution.

Amelanotic Melanoma
- 20% of oral melanomas are non-pigmented
- Oral are of the Acral Lentiginous variety
- Rarely ulcerate

Epulis Granulomatosum
- histologically identical to pyogenic granuloma
- occurs within the socket of a recently extracted tooth
- hyperplastic growth of granulation tissue

Fibrous Dysplasia
Developmental; post-zygotic mutation of GNAS1 gene. Monostotic (late mutation), Polyostotic (intermediate mutation), Syndromic (early mutation).
- Polyostotic may affect just craniofacial bones.
- “Ground glass” radiopaque appearance to bone expansion. Ill-defined borders.
- Syndromes:
- McCune-Albright (FD, café au lait pigmentations (coast of Maine), endocrinopathies)
- Jaffe-Lichtenstein (FD, café au lait pigmentations).
- Growth often continues through adolescence, then slows/stops in adulthood. Lesions may need to be debulked periodically.

Cherubism
- presents in Kids
- multiple quadrants of CGCL
- often resolves in adulthood, sometimes not.

Thyroglossal Duct Cyst
o Midline of neck, anywhere from foramen cecum (base of tongue) down to thyroid.
o Usually attached to hyoid bone; cyst moves when patient swallows.
o Surgical procedure is Sistrunk procedure: remove cyst and involved portion of hyoid bone.
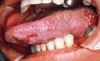
Epstein Barr
- HHV-4