:P Flashcards
(50 cards)
which of the following glial cells making neurotrophic factors?
satellite cells
schwann cells
astrocyte
ependymal cells
oligodendrocytes
which of the following glial cells making neurotrophic factors?
satellite cells
schwann cells
astrocyte
ependymal cells
oligodendrocytes
where do you find the cell body of motor neuron? [1]
where do you find the cell bodys preganglionic autonomic neurons? [1]
where do you find the cell body of motor neuron? [1]
grey matter of ventral horn
where do you find the cell bodys preganglionic autonomic neurons? [1]
lateral horn

what are A & B? [2]
what do A & B connect? [2]
what are their roles? [1]

what are A & B? [2]
A = anterior commisure
B = internal capsule
what do A & B connect? [2]
A = temporal lobes
B = lenticular nucleus & thalamus

what are A & B? [2]
what do A & B connect? [2]
what are their roles? [1]

what are A & B? [2]
A = anterior commisure
B = internal capsule
what do A & B connect? [2]
A = temporal lobes
B = lenticular nucleus & thalamus

where do u find the nuclei in brainstem of nerves that are for:
a) sensory
b) motor
c) mixed
where do u find the nuclei in brainstem of nerves that are for:
a) sensory: lateral
b) motor: medial
c) mixed: middle
what causes, during development , the differentiated nerve fibre capsules? [1]
cytokines are released from the bare end of the nerve fibre and stimulate local CT to for a capsule around it
why are free nerve endings described as polymodal nociceptors?
free nerve endings detect chemical stimuli as well as mechanical displacement
v often produce sensation of pain
which of the following types of myelination would cause slow pain from the skin or act as thermoreceptors?
Aα
Aβ
Aγ
Aδ
C
which of the following types of myelination would cause slow pain from the skin or act as thermoreceptors?
Aα
Aβ
Aγ
Aδ
C
explain mechanism of what occurs after nerve injury xox
- peripheral nerve is cut
- schwann cell wraps around distal part to form continuous line of cells (and make a tunnel)
- proximal end: nerve fibres form growth cones: grow back down inside the sheath
- in growth cone, have filopodia, (contain actin)
- filopodia adhere to the cell adhesion molecules on inner surface of schwann cells, contract and pull forward along tunnel
- schwann cells wrap myeline around nerve fibre
- nerve fibres regen at 1.5mm/ day









label A-E
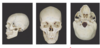
A: temporal
B: sphenoid
C: ethmoid
D: occipital bone
E: temporal bone

what is

ethmoid bone - purple
sphenoid bone - red
zygomatic bone - yellow

which foramen do the followng leave the skull from?
trigeminal nerve
- opthamalic (V1)
- maxillary (V2)
- mandibular (V3)
which foramen do the followng leave the skull from?
trigeminal nerve
- opthamalic (V1): supraorbital foramen
- maxillary (V2): infraoribal foramen
- mandibular (V3): mental foramen

which foramen does the facial nerve exit the skull via? [1]
what does the facial nerve innervate? [1]
which foramen does the facial nerve exit the skull via? [1]
stylomastoid foramen
what does the facial nerve innervate? [1]
motor muscles of facial expression
which foramen does the facial nerve exit the skull via? [1]
what does the facial nerve innervate? [1]
which foramen does the facial nerve exit the skull via? [1]
stylomastoid foramen
what does the facial nerve innervate? [1]
motor muscles of facial expression
spinal accessory nerves leave the skull via which foramen?
formen spinosum
carotid canal
jugular foramen
foramen lacerum
foreman magnum
spinal accessory nerves leave the skull via which foramen?
formen spinosum
carotid canal
jugular foramen
foramen lacerum
foreman magnum
which space do you take lumbar puncture from? [1]
which space do you take an epidural from? [1]
which space do you take lumbar puncture from? [1]
subarachnoid - take CSF
which space do you take an epidural from? [1]
epidural
which of the following is a sensory neuron?
which of the following is a motor neuron?

which of the following is a sensory neuron?
B
which of the following is a motor neuron?
A
where do you find enlargements of spinal cord? [2]
what is conus medularis? [1]
what level is conus medularis? [1]
what level is cauda equina? [1]
what is centre of cauda equina? [1]
where do you find enlargements of spinal cord? [2]
cervical englargement
lumbosacral englargement
(nerves going to limbs)
what is conus medularis? [1]
is the tapered, lower end of the spinal cord.
what level is conus medularis? [1]
L1/L2
what level is cauda equina? [1]
The cauda equina is the sack of nerve roots (nerves that leave the spinal cord between spaces in the bones of the spine to connect to other parts of the body) at the lower end of the spinal cord
what is centre of cauda equina? [1]
l2/l3
where do you find enlargements of spinal cord? [2]
what is conus medularis? [1]
what level is conus medularis? [1]
what level is cauda equina? [1]
what is centre of cauda equina? [1]
where do you find enlargements of spinal cord? [2]
cervical englargement
lumbosacral englargement
(nerves going to limbs)
what is conus medularis? [1]
is the tapered, lower end of the spinal cord.
what level is conus medularis? [1]
L1/L2
what level is cauda equina? [1]
The cauda equina is the sack of nerve roots (nerves that leave the spinal cord between spaces in the bones of the spine to connect to other parts of the body) at the lower end of the spinal cord
what is centre of cauda equina? [1]
l2/l3
how does path of dorsal column medial lemniscus differ if sensory input is from hand / foot? [2]
how does path of dorsal column medial lemniscus differ if sensory input is from hand / foot? [2]
- *differ on which part of the dorsal column medial lemniscus they travel up:**
- Lower body / limb: fasiculus gracilis - more medial
- upper body / limb: fasiculus cuneatus - more lateral