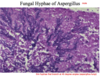
Path 3 Flashcards
(35 cards)

Acute (short/days, neutrophils, edema, no fibrosis, vasodilation & permeability, fever, leukocytosis)
Chronic (long/weeks-months, lymphocytes & plasma cells, ?edema, fibrosis, neovascularization, granulation tissue, low grade fever, anemia, wt loss)


center w/ caseation necrosis
Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection


epithelioid histiocytes (macrophages) forming multinucleated Langhans Giant cells

normal lung


normal lung


normal lung

bronchopneumonia
- atypical pneumonia
- follows distribution of bronchi & bronchioles (patchy)
- staph aureus, klebsiella (abscess formation),
e. coli, pseudomonas, nosocomial pna



acute bronchopneumonia

acute bronchopneumonia

acute lobar pneumonia
- solid congestion, almost entirety of lung lobe
- less common than bronchopna
- pneumococcus (strep pneumoniae)

acute lobar pneumonia



acute pneumonia


bronchopneumonia

lobar pneumonia


lobar pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia
- usually occurs in Rt lung d/t more vertical Rt main bronchus
- type of bronchopneumonia


aspiration pna
-foreign bodies/aspirated material found w/in multinucleated giant cells/macrophages


Complications of PNA
- lung abscesses
- Empyema (pus in pleural cavity)
- Organization of exudates w/ pulmonary fibrosis
- Sepsis
- E.g. of lung abscess


lung abscess, cavitation

Lung abscess


Ghon complex, primary TB

secondary TB