Pictures Flashcards
(125 cards)
1
Q

A
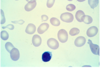
normal red blood cells
2
Q

A
eosinophil
3
Q

A
basophil
4
Q

A
monocyte
5
Q

A
lymphocyte
6
Q

A
lymphocyte
7
Q

A
reactive lymphocyte
8
Q

A
large granular lymphocyte
(NK cell or cytotoxic T cell)
9
Q

A
neutrophil
10
Q
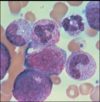
A
left shift: neutrophil variants
horseshoe nuclei: band
bean nuclei: metamyelocytes
round nuclei: myelocyte
11
Q

A
neutrophil with toxic granulation
12
Q

A
platelet
13
Q

A
giant platelet
14
Q
Describe RBC

A
normocytic, normochromic RBC
15
Q
Describe RBC
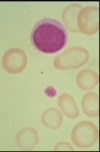
A
hypochromic RBC
16
Q
Describe RBC

A
Hypochromia, anisocytosis, poikilocytosis
17
Q

A
polychromasia
18
Q

A
sickle cell
19
Q

A
Bite cells and hemoglobin clumps
20
Q

A
schistocytes
21
Q

A
blast
22
Q

A
promyelocyte
23
Q

A
myelocyte
24
Q

A
metamyelocyte
25

band
26
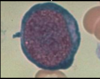
pronormoblast
27

basophilic erythroblast
28

polychromatophilic
29

normochromic erythroblast
30

immature megakaryocyte
31

mature megakaryocyte
32

bone marrow core biopsy (5 year old)
33

bone marrow core biopsy (35 years old)
34

bone marrow core biopsy
top circle: erythroid
bottom circle: myeloid
arrow: megakaryoctye
35

normal bone marrow
36
Describe.
Name.
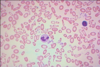
1. microcytosis, hypochromia, anisocytosis, poikilocytosis
2. Iron deficiency
37
Describe.
Name.

1. microcytosis, hypochromia, target cells
2. beta thalasemia
38
Describe.
Name.

1. impaired nuclear maturation indicated by red nucleus, enhanced cytoplasm
2. meagaloblastic RBCs
39
What is this and what causes it?

1. megoblastic anemia
2. impaired B12 uptake, folate deficiency, some drugs, bone marrow dysfunction
40
Describe.
Name.

1. normocytic, iron
2. anemia of chronic infection
41
Describe.
Name.

1. spherocytes
2. hereditary spherocytosis
42
Describe.
Name.
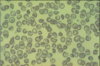
1. hemoglobin crystals
2. Hemoglobin C disease
43
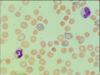
polychromasia (increased reticulocytes)
44
Describe.
Name.
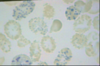
1. heinz bodies
2. G6PD deficiency
45

1. cell that looks like it has a blister
2. G6PD deficiency
46
1. Left arrows
2. Upper right arrows
What is this?

1. merozoites
2. gametocyte
3. Plasmodium falciparum
47

Plasmodium vivax
48

babesia
49

Bartonella bacilliformis
50

Bartonella bacilliformis
51

C. perfringens
52
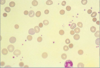
Warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia
53
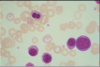
Warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia
54
Describe.
Name.

1. red cell agglutination
2. cold autoimmune hemolytic anemia
55
Describe.
Name.

1. schistocytes
2. microangiopathic hemolytic anemia due to thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura
56

hypersegmented neurtrophil
megaloblastic anemia
57

megaloblastic anemia
A and C: abnormally large erythroid progenitors
B: megaloblast
58

Iron Deficiency
59

hemochromatosis
60

angular cheilosis: ulceration at corners of mouth
iron-deficiency
61

koilonychia: spooning nails (concave, rigid, brittle)
iron-deficiency
62
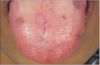
glossitis: bald fissured appearance caused by flattening and loss of papillae
Iron-deficiency
63

iron deficiency:
hypochromic, microcytic, poikilocytes, pencil cells, occasional target cells, plenty of platelets
64
Bone marrow: Perl's stain

normal iron stores: blue
65
Bone marrow: Perl's stain

iron deficiency
no hemosiderin
inset: no siderotic granules in erythroblasts
66

bronzing of skin: due to iron in melanin
hemachromatosis
67
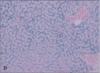
lots of iron in hepatocytes
hematochromatosis
68
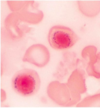
ring sideroblasts with perinuclear ring of iron granules
sideroblastic anemia
69
lead poisoning
causes sideroblastic anemia
70

basophilic stippling: precipitated RNA in RBC
71
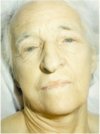
pallor and mild icterus
megaloblastic anemia
72

Glossitis: beefy, red, painful
Megaloblastic anemia: folate deficiency and B12 deficiency
73
Macrocytic RBC
74

hypersegemented neutrophil
megaloblastic anemia
75

Cracked Erythroblast: megaloblastic anemia
76

demyelation of the lateral (pyrimidal) and posterior columns
B12 deficiency: severe neuropathy at this stage
77

sickle cell anemia
78

top: Spleen in sickle cell disease (low power). Red pulp cords and sinusoids are markedly congested; between the congested areas, pale areas of fibrosis resulting from ischemic damage are evident.
bottom: Under high power, splenic sinusoids are dilated and filled with sickled red cells.
79

infarcted spleen due to sickle cell anemia
80

Thalassemia. X-ray film of the skull showing new bone formation on the outer table, producing perpendicular radiations resembling a crewcut.
81

facial abnormalities seen in beta thalassemia
bossing of skull, hypertrophy of maxilla, exposing upper teeth, depression of nasal bridge, periorbital puffiness
82

Expanded marrow in Skull: Beta thalassemia
83

osteoporosis: Beta thalassemia
84
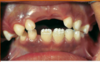
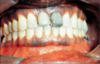
splayed teeth due to widening of the maxilla and mandible
Beta thalassemia
85

Beta thalassemia
pallor, short, massive spleen, wasted limbs
86

ulcer: can occur in all types of hereditary anemias including sickle cell, B-thalassemia, hereditary spherocytosis
87
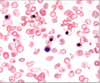
B-Thalassemia major
nucleated RBC, microcytosis, hypochromasia, target cells, teardrop cells, fragments, basophilic stippling
patient short of breath: look for heart failure due to iron load (freq. transfusions)
88

thalassemia trait
microcytosis, hypochromasia, target cells, teardrop cells, rare fragments
low MCV/MCh and increased RDW helps distinguish from iron deficiency
89

B-Thalassemia
fibrosis in portal tracts and nodular regeneration of hepatic parencymal cells, lots of iron
90

B-Thalassemia with pre-existing hep Ccarcinoma on left, and hepatic cirrhosis on right
91

hepatomegaly, heart failure, splenomegaly, edema, die
hydrops fetalis (gamma4)
92

alpha-thalassemia: HbH
deposits: precipitated alpha globin chains and golf ball cells
93

HbH
right: inclusion body (golfball with deposits-\> beta tetramers)
left: reticulocyte
94

HbH
microcytosis, hypochromasia, target cells, microspherocytes, fragments, some basophilic stippling may occur
95

sickle cell anemia
deep stained sickle cells, target cells, polychromasia, hypochromic
96

sickle cell anemia
left: dactylitis
right: leading to shortened fingers in adulthood
97

sickle cell anemia
shortened finger due to dactylitis in childhood
98

sickle cell anemia
right middle metacarpal bone shortened due to infarction of growing epiphysis in childhood
99

pelvis necrosis, flattening of femoral heads
sickle cell anemia
100

sickle cell anemia: chest syndrome
alveolar edema and fat cell embolism
101

Sickle Cell/ hemoglobin C disease
102

teleangiectasia: vascular malformations on face, lips and hands
can get in iron deficiency
103

iron deficiency
smooth, shiny, red tongue and koilonychia (spoon nails)
104

normal RBCs
105

target cells
106
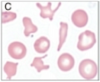
acanthocytes: spur cells
107

echinocytes: burr cells
108

dacrocytes: tear drops
109
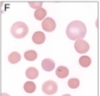
spherocytes
110

ovalocytes
111

blister cells at arrows
112

bite cells
113

schistocytes
114

sickle cells
115

dehydration effect of RBC
116

Howell-Jolly bodies
117

nucleated RBC precursors
118

pappenheimer bodies
119

trophozoites of Plasmodium vivax
120

coarse basophilic stippling of lead poisoning
121

heinz bodies in person with spleen removed
122

B12 deficiency
giant hypersegemented neutrophil
123

hypersegmented neutrophils from antifolate chemo
124

myelodysplastic syndrome
dysplastic neutrophil (pseudopelgeroid cell)
125

degenerating neutrophil


