Respiratory Flashcards
(25 cards)
What is seretide?
ICS + LABA
Fluticasone proprionate + salmeterol
(Think: ‘tide’ means has a steroid)
Available doses are 50/25, 125/25 or 250/25 micrograms
What is spiriva?
LAMA
Tiotropium
Dose = 2.5 microgram inhaled BD
Think: seretide + spiriva = triple therapy!
What is symbicort?
ICS + LABA
Budesonide with formoterol
think cort = cortisone
MDI/DPI 200/6 micrograms, 2 inhalations twice daily.
DPI 400/12 micrograms, 1 inhalation twice daily.
what is breo ellipta?
ICS + LABA
Fluticasone furoate with vilanterol
How do you diagnose obstruction on PFTs?
- If FEV1/FVC < 70% obstruction is present
- If FVC > 80% - pure obstruction
- If either FEV1 or FVC change is > 12% AND 200mL = reversibility
- If FEV1/FVC < 70% obstruction is present
- If FVC < 80% - POSSIBLY MIXED…. but need to confirm on TLC
- (If TLC is REDUCED then mixed with obstruction/resiriction)
- If TLC INCREASED there is likely hyperinflation
- Often RV increases to a greater % than TLC –> gas trapping
- If RV/TLC ratio is increased –> gas trapping

How would you diagnose restrictive lung disease on PFTs?
- If FEV1/FVC > 70% this is normal
- But if FVC < 80% this is suggestive of restriction
- Check by looking at TLC if this is < LLN (dependent on height/weight) = restriction
- Then check DLCO
- If DLCO > normal = extrinsic restirction
- If DLCO < normal = intrinsic restriction

Spiel to QUIT smoking
Non-pharmacological therapy
- Assess barriers to quiting / triggers to smoke
- Enlist help from family, GP, QUIT line
- Set a quit date
- Arrange follow up
Pharmacological therapy (always offer if high nicotine dependence)
- NRT (not in iHD, arrythmia, angina)
- Varenicline (not in schizophrenia, ESKD)
- Buproprion (not in seizures)
- Nortriptyline

What are the causes of clubbing?
What does systemic sclerosis cause?
Causes of clubbing:
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF)
- Asbestosis
- Bronchiectasis.
- Suppurative lung diseases eg cystic fibrosis
- Lung cancer
- Also:
- thyroid disease
- CLD
- cyanotic heart disease
- IE
- IBD
- Coeliac
- HIV
- TB
Systemic sclerosis can cause pseudo clubbing due to loss of pulp / finger atroptht
Name for reduced mouth aperture?
Microstomia
What does a BLSTx scar look like?
Clamshell
(joined in the middle)

What is normal chest expansion?
What causes reduced asymmetrical or symmetrical lung expansion?
Normal expansion
- symmetrical
- 5 - 10 cm
Asymmetrical expansion:
- Unilateral lung disease
- Lung resection
- Pneumonectomy
- Unilateral lung transplantation with normal expansion of the transplanted lung and reduced expansion of the native lung.
Symmetrical but reduced:
- Chronic obstructive lung disease.
- Interstitial lung disease.
How can you tell the difference between lung consolidation / collapse and pleural effusion on examination?
Lung consolidation / collapse:
- Dull percussion note
- Increased vocal tranmission / resonance
- Bronchial breath sounds
Pleural effusion
- (Stony) dull percussion note
- Reduced vocal transmission / resonance
- May have bronchial breath sounds if collapse/consolidation under the effusion
What are the types of quality of breath sounds?
Vesicular = normal
Think: vesicular = alveoli
Normal to hear this over most of the lung
Insp > expiration
Gap between inspiration and expiration (because alveoli are filled)
Soft
Bronchial
Making the sound it would through the bronchi, but if heard through the lungs it means the alveoli are clogged up
Expiration > inspiration, with no gap between (think: going through a tube)
Loud
Often he

What alters the intensity of breath sounds?
Reduced intensity of breath sounds (don’t say ‘reduced air entry’)
- asymmetrical = obstruction
- symmetrical = COPD, pleural effusion, PTx
What are the adventitious breath sounds?
- Crackles / crepitations = inspiratory
- Fine crackles = ILD, pulmonary oedema
- Coarse crackles = LRTI, atelectasis
- Wheeze = expiratory
- Usually polyphonic
- Monophonic = fixed obstruction

What causes lower lobe fibrosis on imaging?
ILD
CTDs (other than AS)
Drugs
Asbestosis
Differentials for tricky to control asthma and their treatment?
Think of different phenotypes
ABPA (also present in CF)
- Allergic reaction to aspergillus
- Daily production of mucopurulent and tenacious sputum lasting months to years
- Other Sx: dyspnea, hemoptysis, wheezing, and pleuritic chest pain
- Dx: serum specific IgE to Aspergillus, precipitans to Aspergillus
- Rx: steroids and antifungals
Allergic asthma with raised IgE
- Rx with omalizumab
Asthma with eosinophilia
- Rx with mepolizumab (against IL-5)
Heart borders on a CXR

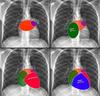
How to identify pulmonary trunk on CXR?

ABove the left main bronchus but below the aortic knuckle

Features of right atrial enlargement on a chest xray?
Occupies more of the retrosternal space

How to identify the heart borders on a lateral chest xray?

Right heart border anteriorly
Left atrium posteriorly at the top, ventircle down the bottom
(remember they are closest to the oesophagus)

What are the radiological criteria for UIP?
Definite:
- Subpleural (around the edges), basal (down the bottom) i.e. an apicobasal gradient (worse down the bottom of the lung)
- Reticular
- Honeycombing (think: sweet - I have the DDx!, not groundglass - shattered, I can’t make the Dx)
- Absence of atypical features

What are the differences in HRCT in non-specific interstitial pneumonia, compared to UIP?
Why is it important to differentiatie between the two?
In NSIP, there is ground glass change, traction bronciectasis, sub-pleural sparing and little honeycombing.
Much better prognosis in NSIP compared to UIP IPF.