Spinal Cord and Nerves Flashcards
(46 cards)
What does the Spinal Cord do?
- Provides a vital link between the brain and the rest of the body
- Exhibits some functional independence from the brain
- Spinal cord and its attached spinal nerves serve two important functions
- Pathway for sensory and motor impulses
- reponsible for reflexes
Development of Spinal Cord
- Develops from ectoderm(neuroectoderm/neuroepithelium) as neural plate
- Neural groove forms in neural plate
- as groove formation progresses, a neural tube is eventually formed
- As the walls of the neural tube thicken, a shallow groove forms that will delineate the anterior(ventral)- posterior(dorsal) axis
- dorsal plate=alar plate(dorsal horn/sensory)
- Ventral plate= basal plate(ventral horn/motor)

Real Texans Drink Cold Beer
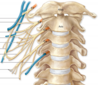
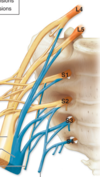
- Refers to the Brachial Plexus and how it’s setup anatomically
- Roots(C5-T1)
- Trunks(superior,middle,inferior)
- Division(3 anterior, 3 posterior)
- Cods(lateral,posterior, median)
- Branches(musculocutaneous, axillary, radial, median, ulnar)
Anatomy of hte Spinal Cord
- Long flattened cylinder
- 2 enlargements:
- Cervical
- lumbar
- 31 Pairs of spinal nerves
CNS at 3 months old
- Cervical and lumbar enlargements visible
- Spinal Cord portion of CNS well distinguised from brain and brainstem regions
- 3 month old,cervical and lumbar enlargements are already in place
- most of the connections are placed as well with the body and what not
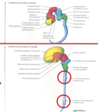
What are the regions associated with the spinal cord and their functions ?
- Cervical
- Cervical plexus
- network of nerves that is a combination of nerves that serve muscle and neck for the most part
- Brachial plexus-innervates the shoulder and upper region, also part of pectoral region and back muscle
- Cervical plexus
- thoracic
- Thoracic symptahetic outflow
- intercostal nerves-long single pair of nerves that go in between ribs
- Lumbar
- lumbar sympathetic outflow
- Lumbosacral enlargement
- Lumbar plexus and sacral plexus merge together and provide innervation to hte pelvis and lower limb strucutre
- Lumbar plexus
- Sacral Plexus
- Sacral parasympathetic outflow-comes from some cranial nerves
- Sacral
- Sacral Parasympathetic outflow
Meningeal coverings in the spinal cord
Dura mater-external to the arachonoic mater , thick and tough layer
- dura mater of the brain is intimately reltaed to the internal aspect of hte bone of the surrounding neurocranium
- Dura mater of the spinal cord seperated from the surrounding bone of the vertebral column by a fat filled epidural space
Arachnoid Mater - well adhere to the dura matter and creates a space
- CSF located between the pia mater and the arachnoid mater
Pia mater -adhered to the spinal cord itself
- Denticulate ligaments
- projection of pia mater that help anchor insdie the dura matter and help attach the arachnoid mater to the dura mater
- Filum terminalis
Spaces in the spinal cord
- Subdural space-between the arachnoid mater and dura mater
- not where the cerebrum spinal fluid flows
- Subarachnoic space-where cerebral spinal fluid flows
- epidural space
Processes in the spinal cord
- Anterior rootlets
- Anterior root
- Posterior rootlets
- Posterior root
- spinal ganglion
- Posterior root
- Spinal nerve
- Anterior ramus
- Posterior ramus
- Gray rami rami communicantes
- White rami communicantes
- Roots only contain either motor or sensory for spinal nerve
- Rami contain both motor and sensory for the spinal nerve

Where do spinal nerves exit the body?
Intra vertebral venous plexus
- Spinal nerve:
- Ventral ramus is hte bottom part
- Dorsal ramus-top part and ramus means branch
Conus medularis
Cauda equina
- Conus Medularis
- Tapered,lower end fo hte spinal cord between L1 and L2 and eventually branches out to the cauda equina
- Cauda equina
- there is one strang that is lighter then the others coming from the tip the pyllum terminallis
- functions like connective tissue , anchors end of hte spinal cord and goes all the way down to the sacrum
- made of pia matter
- Inferior projection of pia matter, off the tip of the conus medullaris
- functions like connective tissue , anchors end of hte spinal cord and goes all the way down to the sacrum
- innervate the pelvic region and hte hips
- Bundle of nerve fibers that connect to a lot of the lower anatomy
- there is one strang that is lighter then the others coming from the tip the pyllum terminallis
Multipolar motor nuerons
- Two or more dendrites and a single axon that may have one or more collateral branches
- most common type in the nervous system
- all of motor neurons that control skeletal muscle and those in ANS
Pseudounipolar Sensory neurons
- Short apparently signal process extending from the cell body
- common process seperates into a peripheral process, conducting impulses from receptor organ toward the cell body into the CNS
- Part of PNS
Grey matter
White matter
- nerve cell bodies lie within and constitue this area of the brain and spinal cord in tranverse sections of the spinal cord, gray matter appears roughly as an H-shaped area embedded in a matrix of white matter
- Supports of hte H are horns
- White matter is the interconnecting fiber tract systems
PNS
- Consists of nerve fibers and cell bodies outside the CNS that conduct impulses to or away from the CNS
- organized into nerves that connect the CNS with peripheral strucutre
Neurolemma
- consists of cell membranes of Schwann cells that immediately surround the axon, separating it from other axons
- two forms in the PNS
- myelinated nerve fibers ocnsists of schwann cells specific to an individual axon, organized into a continous series of enwarpping cells that form myelin
- unmyelinated nerve fibers is composed of Schwann cells that do not make up such an apparaten series; multiple axons are separately embedded within the cytoplasm fo each cell
- these cells do not produce myelin and most fibers inthe cutaneous nerves are unmyelinated
- two forms in the PNS
Afferent fibers vs efferent fibers
- afferent fibers(sensory) voncery neural impulses to the CNS from the sense organs and from sensory receptors in various parts of the body
- efferent fibers(motor) convery neural impulses from the CNS to effector organs(muscles and glands)
- nerves either cranial nerves,spinal nerves , or derivatives of them
Cranial nerves
- exit the cranial cavity through foramina(openings) in the cranium and are identified by a descripiptive name or roman numeral
- 11 out 12 pari of cranial nerves arise from teh brain;other pair arises from sueprior part of hte spinal cord(CN XI)
Spinal(segmental) nerves
- Exit the vertebral column through intervetrebral foramina
- arise in bilateral pairs from a specific segment of hte spinal cord
- 31 spinal cord segments and 31 pair of nerves arising from them are identified by a letter and number
- Designating region fo the spinal cord and their superior to inferior order
- C,cervical; T , thoracic; L , Lumbar; S , sacral; Co, Coccygeal
- C1-C8
- T1-T12
- L1-L5
- S1-S5
- Initially arise from spinal cord as rootlets which converge to form two nerve roots
Anterior vs Posterior nerve root
- Anterior(ventral)=consisting of motor (efferent) fibers passing from nerve cell bodies in the anterior horn of spinal cord gray matter to effector organs located peripherally
- Posterior=consisting of sensory(afferent) fibers from cell bodies in the spinal(sensory) or posterior(dorsal) root gnaglion that extend peripherally to sensory endings and centrally to the posterior horn of hte spinal cord gray matter
- Posterior and Anterior nerve roots untie close to the intervetrebral foramen , to form a mixed spinal nerve
- This immediately divides into two rami:posterior and anterior ramus
Dermatome and myotome
- Dermatome-unilateral area of skin innervated by the sensory fibers of a single spinal nerve
- Think of spinal nerve roots as highly segemented into dermatomes in the body, but then the nerves themselves are more widely distributed and are made up of these spinal vertaberates( this is what plexus are about)
- myotome-uniltaeral muscle mass receiving innervation from the fibers convey by a single spinal nerve
- genrally at least two adjacent spinal nerves(or posterior roots) must be interrupted to produce a discernible area of numbness
- lesion on one spot will do nothing
- genrally at least two adjacent spinal nerves(or posterior roots) must be interrupted to produce a discernible area of numbness
Posterior(primary) rami of spinal nerves
- Supply neve fibers to
- Synovial joints of hte vertebral column
- deep muscles of the back
- overlying skin in segmental pattern
- General rule remain separate from each other(do not merge to form major somatic nerve plexuses)
Anterior(primary) rami of spinal nerves
- Supply nerve fibers to the much larger remaining area consists of:
- Anterior and lateral regions of hte trunk
- Upper and lower limbs
- Muscle and limbs in segmental pattern
- Distributed exclusiverly to the trunk generaly remain separae from each other
- majority of anterior rami merge with one or more adjacent anterior rami to form major somatic nerve plexus (networks)
Somatic Fibers and motor
- General sensory fibers-transmit sensations from the body to the CNS
- May be exteroceptive sensations from the skin or pain
- proprioreceptive sensations from muscles, tendons and joints
- Usually subconscious providing information regarding joint position and tension of tendons and muscles
- combined with the vestibular appartus of the internal ear helps with orientation of hte body
- Somatic motor fiber-transmit impulses to the skeletal muscles