Week 1: Brain and Spinal Cord Flashcards
(41 cards)
Coronally, the white matter is organized ___ the grey matter, more “____” the brain.
The white matter tracts in the spinal cord are on the “___,” (Ie, they switch organizations), with grey matter in the ___ surface.
Coronally, the white matter is organized below the grey matter, more “inside” the brain.
The white matter tracts in the spinal cord are on the “outside,” (Ie, they switch organizations), with grey matter in the interior surface.
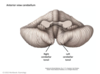
homunculus:
feet and legs are represented medially next to the ___ __ fissure. Theb bodies are represented on the superior-medial surface, and the hands are __ to that, the face is also __. The pharyngeal structures are inferior, near the __ __.
feet and legs are represented medially next to the longitudinal cerebral fissure. Theb bodies are represented on the superior-medial surface, and the hands are lateral to that, the face is also lateral. The pharyngeal structures are inferior, near the sylvian fissure.
these two arrows make up the

diencephalon



what consists of the limbic system
cingulate gyrus, fornix, hippocampus and amygdala
two componens of the diencephalon
thalamus and hypothalamus
three components of hindbrain
cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata
three components of the midbrain
superior and inferior colliculus and tegmentum


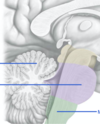

two layers of the dura
endosteal (connects to the skull)
meningeal (connects to the arachnoid mater
the later with a webby appearance, named for spider web. Overlays the cerebral arteries and veins, and cerebral gyri and sulci.
arachnoid mater
There are ___ vertebrae in the vertebral column, divided into 5 regions; cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal.
There are 33 vertebrae in the vertebral column, divided into 5 regions; cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal.
The atlas has a superior articular surface facet that articulates with the __ __ of the skull
The atlas has a superior articular surface facet that articulates with the occipital condyles of the skull

The spinal cord has ___pairs of spinal nerves. Each with ___ motor fibers and ___ sensory fibres composed of multiple rootlets.
The spinal cord has 31 pairs of spinal nerves. Each with anterior motor fibers and posterior sensory fibres composed of multiple rootlets.
The cord itself ends around L1-l2, called the ___ ___. Below the level of T12, the spinal nerves form a region called __ __.
The cord itself ends around L1-l2, called the conus medullaris. Below the level of T12, the spinal nerves form a region called cauda equina.
meningeal layer:
Arachnoid is the middle layer and held against the dura by ___ from the __
Arachnoid is the middle layer and held against the dura by pressure from the CSF


- the __ __ houses the cell body of the sensory neurons. It’s also called the dorsal/posterior root ganglion/sensory root ganglion.
- the spinal ganglion houses the cell body of the sensory neurons. It’s also called the dorsal/posterior root ganglion/sensory root ganglion.

which pathway is in each segment of the spinal cord


how many neurons in a somatic motor pathway
somatic motor pathway ie/ corticospinal or corticobulbar. There are 2 parts; UMN and LMN
In the corticospinal pathway: info goes from the CNS out to the body
In the corticobulbar pathways; fibers carry infro from the CNS to the face structures, involving the cranial nerves.
There are horizontal pathways, both from the cerebellum and from the basal ganglia to modulate the main pathways
Corticospinal Pathway
__ is where the cell bodies of the UMN of the corticospinal paths originate. From these cell bodies, axons descend into the cortex, where they converge to form the _- __, and pass through the __ __ of the internal capsule inferiorly.
the UMN then moves towards the __ __/crus cerebri, doesn into the __, and then to the ___ __, where the UMN __.
The UMN continues to move down to the __ __, and it SYNAPSES with the LMN in the __ __
PMC is where the cell bodies of the UMN of the corticospinal paths originate. From these cell bodies, axons descend into the cortex, where they converge to form the corona radiata, and pass through the posterior limb of the internal capsule inferiorly.
the UMN then moves towards the cerebral peduncles/crus cerebri, doesn into the pons, and then to the mmedullary pyramids, where the UMN DECUSSATES.
The UMN continues to move down to the spinal cord, and it SYNAPSES with the LMN in the ANTERIOR HORN
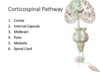
outline the different aspects of the internal capsule
posterior capsule; contains corticospinal lumb fibers (descending)
Genu; carries cortical bulbar tract spinals
Anterior limb fibers (cognitive processes, probably discussed in course

Outline the corticobulbar pathway
There fibers can be traced inferiorly from the corte, to the internal capsule (travelling through the genu of the internal capsule), and then down to the brainstem, where they synapse to a bunch of cranial nerves (or decussate before synapsing to cranial nerves)
At the cranial nerve level, they exit to innervate the head and neck structures.