Week 3: Skull, Brainstem and Cranial Nerve Flashcards
(89 cards)
outline hthe bones of the vsicerl cranium
Aka the facial skeleton-- Nasal bones; make up the bridge of the nose
The paired maxillary bones make up the upper jaw, floor of the orbit and parts of nose and hard palate
Mandible forms lower jaw and houses the lower teeth
Paired zygomatic bone; lateral aspects of orbit and bony processes of the cheek (cheek bones)
The zygomatic also joins the temporal bone to form the zygomatic arch.

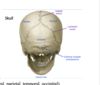
what bone of the skull is associated with the mastoid process
temporal
what is the largest fontanelle in children
The largest fontanelle is the anterior fontanelle, which is between the frontal and parietal bones, and closes between 18-24 mos of age.
The coronal suture runs between the frontal and parietal bones.
The sagittal suture runs between the two parietal bones, and meets with the two lateral lambdoid sutures, which separates the parietal bones from the occipital bone of the skull.
The external occipital protuberance is a key landmark and can be felt posteriorly on the skull. It’s the attachment site for a number of neck muscle.
suture line between occipital and parietal
lamboid
suture line between the two aspects of the parietal bones in a fetus
the saggital suture
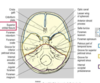
how can fracture of the pterion cause a hematoma? what type of hematoma?
Pterion– worse consequences, formed by the joining of the frontal, parietal, sphenoid and temporal bones. The middle meningeal artery runs between the skull bones and the dura mater at the point of the pterion. A fracture in this region can sever this artery and lead to a life threatening epidural hematoma.


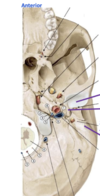
which fossa contains the sella turcica and pituitary gland
middle cranial fossa; hosues the tmpeoral lobe, forms the sella turcica, and contains the pituitary glan
the spinal cord exit hole
foramen magnum

Cribriform plate: has many holes were the extensions of the ___ __ pass through into the nasal cavity.
Cribriform plate: has many holes were the extensions of the olfactory nerve pass through into the nasal cavity.
Optic canal: houses the __ __ as well as some blood supply to the eye.
Optic canal: houses the optic nerve as well as some blood supply to the eye.
what nerves run through the superior orbital fissure?
3, 4, 6, and V1(opthalmic of trigeminal nerve)
what CN runs through the foramen rotundum
the V2 (maxillary nerve)
what CN runs throguh the foramen ovale
V3 (mandibular nerve of the trigeminal nerve)
the foramen spinosum contains the __ ___ artery
middle meningeal artery
what moves through the carotid canal?
internal carotid artery, which tontributes to the circle of willis
what moves throuhg the internal acoustic meatus?
cranial nerve 7 and 8; facial and vestibulocochlear
what nerves move throuhg the jugular foramen?
in addition to the jugular vein, CN 9, 10, 11 also run through the jugular foramen
what moves through the foramen magnum?
vertebral artery travels superiorly to the foramen magnum. lateral to the foramen magnum is the occipital condyle which artculates with the C1 vertebrae. there is a mandibular fossa where the TMJ os lovated.
exit of the facial nerve
the facial nerve (7) runs through the internal acoustic meatus, and also exits out of the stylomastroid foramen.
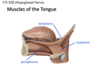
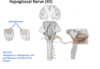
what CN exits the hypoglossal canal?
hypoglossal nerve, which provides motor output for the tongue