WEEK 11 Flashcards
(23 cards)
Social dilemma
Situation in which actions taken independently by self-interested individuals result in a socially suboptimal outcome (e.g. traffic jams, climate change)
Tragedy of the Commons
Resource depletion through collective action through common property and public goods
Process-regarding preferences
Evaluation of a state is conditional on how it came about
Best response
Strategy that yields the highest payoff given the other player’s strategy
Dominant strategy
Best response to all possible strategies of the other player
Dominant strategy equilibrium
Outcome in which everyone plays the dominant strategy
Prisoner’s Dilemma
Game with a dominant strategy equilibrium, in which playing the dominant strategy yields lower individual and total payoffs compared to other strategies
Peer punishment
Ability to identify and punish free-riders, increases individual contributions
Ultimatum game
Sequential game where players choose how to divide up economic rents (e.g. cash prize)
What moves outcomes closer to self-interested outcome?
Introducing competition between responders
Social regarding preferences table

Game table

Prisoner’s dilemma table

Ultimatum game tree diagram
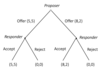
What does a game describing social interactions include?
Nash equilibrium
- Everyone plays the best strategy given the strategies chosen by everyone else
- No one has incentive to deviate unilaterally

Coordination game
- More than one Nash equilibrium
- Individuals choose independently
- Socially optimal outcome may not be selected because there is no incentive to unilaterally change action

Climate change table
n.b. BAU = business as usual
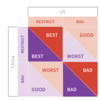
Altruism graph

Prisoner’s Dilemma graph

Why do better outcomes arise from repeated interactions?
- Social norms
- Reciprocity
- Peer punishment
- Behaving selfishly may no longer be dominant strategy
Outcome of public goods game
- People happy to contribute as long as others reciprocate
- Contributions differ according to social norms


