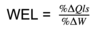WEEK 4 Flashcards
(14 cards)
elasticity
general concept used to quantify the response in one variable when another variable changes
PED
measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in price
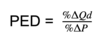
elastic demand
- absolute value > 1
- if price decreases, total revenue and expenditure increase
- if price increases, total revenue and expenditure decrease
inelastic demand
- demand that responds somewhat, but not a great deal, to changes in price
- 1 > absolute value > 0
- if price decreases, total revenue and expenditure decrease
- if price increases, total revenue and expenditure increase
unitary elastic demand
- absolute value = 1
- if price decreases, same total revenue and expenditure
- if price increases, same total revenue and expenditure
perfectly inelastic demand
- demand in which quantity demanded does not respond at all to changes in price
- e.g. insulin
- if price increases by 10%, total revenue and expenditure increase by 10%

perfectly elastic demand
- demand in which quantity demanded drops to 0 with any price increase
- e.g. wheat

- percentage change in quantity demanded equation
- percentage change in price equation

point elasticity along demand curve
n.b. unitary elasticity occurs at the midpoint on the x-axis

determinants of elasticity
- Availability of substitutes (more substitutes = more elastic)
- Percentage of total income (if small percentage then not noticable so more inelastic)
- Time (in long run more elastic)
income elasticity of demand
measure of the responsiveness of demand to changes in income

cross-price elasticity of demand
measure of the responsiveness of one good’s quantity demanded to a change in price of another good

price elasticity of supply
measure of the responsiveness of quantity supplied to changes in price

wage elasticity of labor supply
measure of the responsiveness of labor supplied to changes in wage