WEEK 5 Flashcards
(28 cards)
perfect knowledge
assumption that
- Households possess a knowledge of the qualities and prices available in the market
-
Firms have all available information concerning:
- Wage rates
- Capital costs
- Technology
- Output prices
perfect competition
industry structure in which there are:
- Many firms, each small relative to the industry
- Produce virtually identical productions
- No firm is large enough to have any control over prices
homogenous products
products that are identical/indistinguishable from one another
What are the 3 basic decisions households make in the output market?
- how much of each product to demand
- how much labor to supply
- how much to spend today and how much to save for the future
budget constraint
limits imposed on household choices by
- income
- wealth
- prices
choice/opportunity set
set of options that is limited by a budget constraint

real income
set of opportunities to purchase real goods/services available to a household as determined by price and money income
budget constraint equation
where I = household income

What is the effect of a change in price on budget constraint?
n.b. the opportunity set after the price decrease is both triangles

utility
satisfaction a product yields
marginal utility
additional satisfaction gained by the consumption of one more unit of a g/s
total utility
total amount of satisfaction obtained from consumption of a g/s
law of diminishing marginal utility
the more of any one good consumed in a given period, the less utility generated by consuming each additional unit of the same good
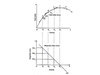
total utility and marginal utility graphs
financial capital market
complex set of institutions in which suppliers of capital (households that save) and demand for capital (firms wanting to invest) interact
What are the assumptions of the indifference curve?
- analysis is restricted to goods with positive marginal utility
- diminishing marginal rate of substitution defined as (see pic) - ratio at which a household is willing to substitute X for Y
- consumers have ability to choose among combinations of g/s available
- consumer choices are consistent (rational)

indifference curve
set of points, each a comination of good X and good Y, that all yield the same total utility
indifference curve graph
- consumer is indifferent between points A,B,C
- however, if at point to the left of the curve then the consumer is unequivocally worse off

indifference curves + budget constraint
highest possible utility curve is at the point where the indifference curve is tangent to the budget constraint

diamond/water paradox
states:
- things with the greatest value in use frequently have little or no value in exchange
- things with the greatest value in exchange frequently have little or no value in use
income effect
- if a household continues to buy the same amount of every g/s after a decrease in the price of one good, it will have income left over
- extra income can be spent on the product whose price declined or on other products
substitution effect
- when the price of a product decreases, the product becomes relatively cheaper and therefore more attractive than substitutes
- household will shift away from substitutes and towards this product
income and substitution effects as demand mechanisms

What are the 3 decisions made by households in input markets?
- whether to work
- how much to work
- what kind of job to work



