Week 4 Flashcards
(129 cards)
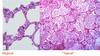
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Location
Histology
Syndrom
Central
Keratin pearls, intracellular bridges
Parathyroid Hormone Related Peptide
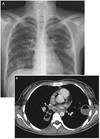
Symptoms of lung cancer
Cough
Hemoptysis
Chest Pain
Pneumonia
Brain Mets
Lung metastasis destination
Brain, adrenal, liver, bone
Lung cancers examples
Squamous cell carcinoma
Adenocarcinoma
Small cell carcinoma
Carcinoid tumor
Large cell carcinoma
Symptoms of paraneoplastic syndrome
Hypercalcemia
Stones and bones
Short QT
Confusion, tired, coma
Muscle weakness
Nausaea and constipation
Tumor in lung apex
Pancostal tumor
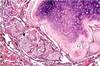
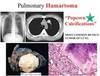
Benign leasions of lungs
Granuloma (TB, fungus, sacro)
Bronchial harmatoma
Another name for brochoalveolar carcinoma
Adenocarcinoma in-situ
Adenocarcinoma
Most common in
Location
Histology
Cells
Mutations
Women / Non-smoker
Periphery
Epithelium with grandular
Type II and clara (peripheral)
KRAS, EGFR, ALK
Adenocarcinoma
treatment:
ALK
EGFR
Gefitinb
Crizotinib
Adenocarinoma
precurors
Adenocarcinoma in-situ (bronchoalveaolar)
Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia
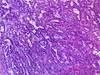
Small Cell Carcinoma
Treatment (general)
Characteristics
Location
Origin
Differentiation
Syndrome
Chemo
Most aggressive
Central
Neuroendocrine
Poorly differentiated
+ADH/+ACTH
Carcinoid tumor
Histology
Orign
Differentiation
Unfirom cell size, round
Neuroendocrine
Well diff
Large cell carcinoma
Diagnosis by
Gross
Diagnosis by exclusion
Large necrotic mass
What lowers aspiration events
Increase in cricoid pressure
Rapid intubation
Use of rapid acting and paralytic meds
Subglottic suctioning
Damage from aspiration
Gram negative bacteria
Acid
How do intubated patients develop pneumonia?
The flora of intubated patient changes to organisms like pseudomonas
Treatment for aspiration
Decontamination - Chlorhexidine - antiseptic esp. gram+
Gentamicin, colistin, vancomycin - europe (resistance??)
The most common nosocomial infection in the ICU
Cause
Organisms
Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP)
Intubation
Gram (-) pseudomonas Gram (+) ORSA
Diagnosis of Pneumonia (Kuhls)
CPIS Score (Clinical Pulmonary Infection Score)
Fever or hypothermia
Leukocytoses or leukopenia
Increased respiratory secretions
New or worsened infiltrate on chest x-ray
Definition of ARDS
Bilateral infiltrate on CXR
Wedge less than 18 no hypetension
Hypoxemia regardless of PEEP
– PO2/iO2F ratio less than 200 (normal 100/0.21=500) (ALI 300 or less)
–
Association with ARDS
Sepsis (most common)
Pancreatitis
Pneumonia
Aspiration
uRemia
Trauma
Amniotic fluid embolism
Shock
Stages of ARDS
Prodrome (12-36h) - CXR mild increase in microvaculatrue, normal pO2, low pCO2, tachypnea, agitation (mediated by neutrophila)
Acute (exudative) phase (up to 7d) - hypoxema, CXR cardiac edema (like cardiogenic), capillary endothelial damage (edema); possible sepsis (lack of barrier) TYPE1, atelectesis (2/2 loss of surfactant) TYPE2
Proliferative (7-10d+) - Collagen deposition, hypercarbia
Fibrosis alveolitits (10+) - alveolar thick, hypercarbia, pul HTN, RHF
Recovery – M recovery PMN death
ARDS treatment
Vasopressors (levophed)
Antibiotics
Increase PEEP to decrease FiO2 (decrease O2 toxcitit)
Low tidal volume ventilation
Rotational therapy