Week 5 Flashcards
(90 cards)
What females have higher rates of UTI and why?
Postmenopausal women have higher rates of infection because of bladder or uterine prolapse and other hormonally induced changes
Cause for increase in UTI in males?
Obstruction of the urethra following development of benign prostatic hypertrophy
Most common cause of uncomplicated UTI in all age group
Second
E. Coli
S. saprophyticus
Causes for complicated UTi (organisms)
E. coli, Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterococcus spp., and Group B streptococci
Cause for granulomatous inflammation in bladder wall
Fungal cause
Schistosoma hematobium
Candida
Host risk factors for UTI
Female
Sex
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Vesicoutheral reflux (bladder ot kidey)
Pregnancy (bladder emptying)
Urethral catheters
Calcui
Where are organisms that cause UTI found in?
feces
Virulence factor that facilitates infection UTI
fimbrae
anti-UTI factors
Urine flow
Uroepithelial cell sloughing,
Types of fibrae
other pathogenic compounds
Type I - bind to mannose; cystitis and pyelonephriits
P Fimbrae - bind to glycosphingolipid; pylonephirits
hemolysin (damage to uroepithelium)
Symptoms of cystitis
urgency and frequency of urination
voiding small volumes of urine (oliguria)
painful urination (dysuria)
suprapubic tenderness just before or
immediately after voiding
Diagnosis of cystitis
uterine pH - dipsitc (not elevated =E.coli / elevated Proteus)
pyuria (WBCs in urine) - leukocyte esterase
bacteriuria (bacteria in urine) - nitrates, clean-catch urine specimen
Cystitis treatment
Most get well without antibiotics
nitrofurantoin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and fosfomycin
When the cystitis treatment is a must?
Pregnant women
Renal transplant
genitourinary tract surgery
Pylonephritits
symptoms
fever (>38° C)
nausea and vomiting
flank pain and tenderness
costovertebral angle tenderness
Alternative route to kideny infection
organism?
pyelonephritis
hematogenous
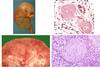
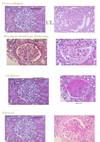
Acute vs. Chronic
pyelonephritis
Acute
the kidney is somewhat enlarged, and discrete, yellowish, raised abscesses are apparent on the surface
neutrophilic infiltrate, suppurative necrosis, and abscess formation
Chronic
chronic tubulointerstitial inflammation and scarring involve the calyces and pelvis
parenchyma shows interstitial fibrosis with an inflammatory infiltrate of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and occasionally neutrophils
Complications of pyelonephritis
Papillary necrosis - diabetics, ssd, urinary tract obstruction
Pyonephrosis - when complete obstrction filling renal pelvis, calyces, and ureter
Perinephric abscess - extension of inflammation through the renal capsule
Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis - chronic pyelonephritis characterized by accumulation of foamy macrophages intermingled with plasma cells, lymphocytes, epithelioid cells, and occasional giant cells (associated with proteus)
Proteus
growth pattern
enzye
formation of
Swarming growth
urease
Struvite calculi
Treatment of pyelonephritis
Prevention
Fluoroquinolone
severe: IV ceftriaxone
High fluid intake ; tannins (cranberry)
Prevention of UTI
No spermicide-containg contraceptives
(post-menapausal) oral or vaginal estorgen
Lactobacilli
Prostatitis
symptoms and tests
Recal exam - swollen (boggy) prostate, warm, tender
PSA testing
midstream catch
ph, leukocyte esterase, nitrates
Prostatitis
treatment
trimethoprim- sulfamethoxazole
Juxtamedullary vs. Cortial nephrone
Juxtamedullary hyperosmotic 600-1200 mOsm
Cortial isosmotic 300 mOsm