Week 5 - finished Flashcards
(81 cards)
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there?
31
What do the dorsal and ventral root join to form? What does this structure later spilt to form?
They join to form the spinal nerve for that segment. This spinal nerve later splits to form the dorsal and ventral rami
What kind of information is transmitted through the dorsal root?
Sensory information
What kind of information is transmitted through the ventral root?
Motor information
What are the names for the thicker sections of the spinal cord which correlate for the upper and lower limbs? Why are they thicker?
The cervical and lumbar enlargements
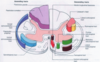
What is grey matter?
Cell bodies
What is white matter?
Axons
What is the function of the dorsal horn grey matter?
Cell bodies for sensory information
What is the function of the ventral horn grey matter?
Cell bodies for motor information
What is the function of the lateral horn grey matter?
Cell bodies for autonomic function
Where is the lateral horn found?
Between the levels of T1-L2-3
What are the separations of white matter called, what makes these separations and what are the 3 regions these separations are named after?
The separations are called funiculi and are divided into these by the horns of grey matter. There are 3 funiculi: Ventral Dorsal Lateral
Briefly describe each of the Laminae of Rexed:
1: AKA marginal zone. 2nd order neurons of the ALS found here. 2: AKA Substantia gelatinosa. 2nd order neurons for ALS found here. 3,4,5,6: AKA Nucleus Proprius. Processing of sensory info, input of nociceptive and other senses from both peripheral and visceral areas. (may explain referred pain) 7: AKA Clarkes nucleus. Only in the thoracic and upper lumbar regions. Relays unconscious proprioceptive information about the limbs to the ipsilateral cerebellum. 8: Contains the interneurons for the regulation of skeletal muscle contraction. 9: LMN’s for skeletal muscle contraction 10: Surround central canal and receives afferent input similar to laminae 1 and 2.
What are A delta fibres?
Myelinated nociceptive fibres
What are A beta fibres?
Large myelinated fibres from mechanoreceptors
What are C fibres?
Unmyelinated fibres from nociceptors
What does the first lamina of rexed do? What is it AKA?
AKA marginal zone. 2nd order neurons of the ALS found here.
What does the second lamina of rexed do? What is it AKA?
AKA Substantia gelatinosa. 2nd order neurons for ALS found here.
What do the 3rd-6th laminae of rexed do? What are they AKA?
AKA Nucleus Proprius. Processing of sensory info, input of nociceptive and other senses from both peripheral and visceral areas. (may explain referred pain)
What does the 7th lamina of rexed do? What is it AKA?
AKA Clarkes nucleus. Only in the thoracic and upper lumbar regions. Relays unconscious proprioceptive information about the limbs to the ipsilateral cerebellum.
What does the 8th lamina of rexed do?
Contains the interneurons for the regulation of skeletal muscle contraction.
What does the 9th lamina of rexed do?
LMN’s for skeletal muscle contraction
What does the 10th lamina of rexed do?
Surround central canal and receives afferent input similar to laminae 1 and 2.
What 3 tracts ascend in the white matter?
DCML ALS Spinocerebellar tracts