EKG pics Flashcards

-
VT
- Wide, bizarre QRS complex
- Not typical LBBB or RBBB complex
-
AV dissociation
- P-waves get in front of the ventricle far enough -→ fusion/capture complex


-
Atrial tachycardia
- P-waves (originating from the low RA, near the AV node)
- negative in II, III, aVF
- positive in I, aVL
- P-waves (originating from the low RA, near the AV node)
- RAD
- no need to code ST-T changes of ischemia


- Atrial Flutter
- AV block, 2:1
- P-wave immediately at the end of the QRS complex
- V-rate ~ 150 bpm


- NSR
-
Brugada Syndrome
- Type I and Type II pattern
- J-point elevation at end of the QRS complex + coved downward ST-segment + inverted T-wave → Type I
- V3 with saddleback ST-elevation → Type II
- not diagnostic if only finding


- NSR
- LVH
- Acute Pericarditis
- Do note code ST-T changes when coding pericarditis


- A-fib
- WPW


- Sinus arrhythmia
- LBBB
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities suggesting myocardial injury
- 1 mm inferior ST-elevation (II and aVF)
- 2-4 mm anterolateral concordant ST-elevation (V4-V5)
- location of acute infarction should not be coded int he presence of a LBBB


- NSR
- AV dissociation
- VVI - normal function
- AV interval at the end of the tracing is longer than at the beginning of the tracing (AV interval has prolonged by approximately 80 msec) indicating the atrial and ventricular rhythms are dissociated and the pacemaker is programmed VVI and not tracking atrial activity


- NSR
- Inferior MI - age recent or probably acute
- Posterior infarction injury pattern cannot be coded:
- R-wave does not exceed S-wave in V1-V2


- A-fib
- PVC’s
- Bi-V pacing
- V-sensed response
- R precordial leads → 2 pacing spikes
-
negative deflection → I and aVL
- activation from LV lead from lateral lead away from left side
- Pacing spike on PVC → designed to force Bi-V pacing and decrease the asynchrony caused by the PVC


- SR
- RAE
- Prolonged QT
- Hypokalemia


- MAT
RAE - not coded as large P-waves are ectopic in origin


- NSR
- Acute Pericarditis
- Pericardial effusion
- Electrical alternans


- NSR
- 2nd Degree AV Block - Mobitz I (Wenckebach)
- AV junctional escape complexes
- Inferior MI - age recent/acute


**29 year old female with dyspnea → Pulmonary hypertension
- NSR
- Sinus arrhythmia
- RAD
- RVH
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities secondary to hypertrophy


****24 year old male with bipolar disorder
- NSR
- PVC’s
- Prolonged QT
- Torsades de pointes
- T-wave becomes more complex following PVC/pause → increases risk of PVC on T wave → Torsades de pointes/malignant long QT


*** 74 year old female with 3 hours of chest pain and dyspnea
- NSR
- PVC’s
- 2nd degree AV block - Mobitz I
- Posterior MI - age recent/acute


***26-year old female with ascites and acute severe dyspnea
- ST
- RAE
- RAD
- RVH
- ST-T abnormalities secondary to hypertrophy
- PE/acute cor pulmonale

Describe the findings

Dual-chamber pacemaker (DDD), normally functioning
- Pacer spikes seen in I and III on the first beats of the tracing

Describe the findings

- A-fib (+4)
- LAD
- RBBB (+2)
- Anterior/anteroseptal age indeterminate/old (+2)
- Inferior age indeterminate/old (+2)

Describe the findings

- PAC’s
- Junctional rhythm/tachycardia (+2)
- LAD
- LVH (+2)
- ST/T abnormalities secondary to hypertrophy

Describe the findings

- NSR
- AIVR (+4)
- AV dissociation (+2)

Describe the findings:
- A-fib
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities suggesting myocardial ischemia

Describe the findings:

- SVT
- PVC’s
- RAD
- IVCD, nonspecific type
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities suggesting myocardial ischemia

EKG Definition:
- LBBB
- Mean QRS duration
- ► 120 ms - Adults
- > 100 ms - Children 4-16 years
- > 90 ms - Children < 4 years
- Late forces of QRS complex should be negative (terminal S wave in V1)
-
Broad notched or slurred R wave in leads I, aVL, V5, V6 and
- occasional RS pattern in V5 and V6 attributed to displaced transition of QRS complex
-
Absent q waves in leads I, V5, V6
- but in lead aVL, a narrow q wave may be present in the absence of myocardial pathology
- Delayed onset of intrinsicoid deflection (> 60 ms from beginning of QRS complex to peak of R wave) in leads V5 and V6 but normal in leads V1-V3 when small initial r waves can be discerned in these leads

Describe the findings:

- Artifact
- NSR
- PVC’s
- RBBB, Complete
- Inferior MI, age indeterminant or probably old

Describe the findings:
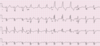
- NSR
- RVH
- in the setting of RBBB –> R-prime in V1 > 15 mm suggests RVH
- RBBB, complete
- Prolonged QT interval
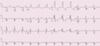
Describe the findings:

- Incorrect electrode placement
- abrupt change in R wave progression in lead V3 with immediate return of R wave forces in lead V4
- Sinus bradycardia (HR < 60 bpm)
- WPW

Describe the findings:

- Normal EKG
- NSR

Describe the findings:

- MAT
- PVC’s
- LVH
- LBBB, complete
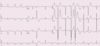
Describe the findings:

- NSR
- RAD
- LA enlargement
- IVCD, nonspecific type
- Pacemaker malfunction, not constantly capturing (atrium or ventricle)
- Pacemaker malfunction, not constantly sensing (atrium or ventricle)

Describe the findings:

- Atrial or coronary sinus pacing
- LVH (female)

Describe the findings:

- AT
- P-waves of sinus node origin should be positive in lead II, not negative as seen here.
- P-wave is secondary to an ectopic atrial focus
- Inferior MI, age indeterminant or probably old

Describe the findings:

- SB
- AV junctional rhythm/tachycardia
- AV dissociaton
- RBBB, complete
- LAFB
****P waves appear closer and closer to each QRS complex, until the P-wave becomes entirely hidden within the QRS complex.
*****P-waves in this tracing are actually not conducting the QRS complexes –> complete AV dissociation
*******When sinus rate is similar to junctional escape rhythm –> isoarrhythmic AV dissociation

Describe the findings:

- ST
- AV junctional rhythm/tachycardia
- AV block, 3rd degree
- Inferior MI, age recent or probably acute

Describe the findings:

- A-fib
- PVC
- Nonspecific ST and/or T wave abnormalities

Describe the findings:

- A-fib
- LAD

Describe the findings:

- NSR
- LA enlargement
- Nonspecific ST and/or T wave abnormalities

Describe the findings

- NSR
- 1st degree AV block
- IVCD, nonspecific
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities suggesting electrolyte disturbances (+2)
- Hyperkalemia (+4)

Describe the findings

- NSR
- RAD (+2)
- RVH (+4)

Describe the findings

- NSR
- PAC’s
- 1st degree AV block
- LBBB (+4)

Describe the findings

- SVT (+4)
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities suggesting myocardial ischemia
- > 1 mm of horizontal or downsloping ST-T segment depression and/or
- T wave inversion greater than or equal to 2 mm

Describe the findings
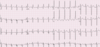
- LA enlargement
- ST
- RAD
-
RVH (+4)
- mean QRS axis > 100 degrees
- R/S ratio in V1 > 1, R/S ratio in V5 or V6 < 1, qR complex in V1, or R wave > 7 mm in V1
- ST and/or T wave abnormalities secondary to hypertrophy
*****42 year old male with history of severe PAH –> resuling in significant RVH

Describe the findings

- NSR
- LAD
- RBBB
- 2nd degree AV block - Type I (Wenckebach)
- Inferior MI, age old or indeterminate

Describe the findings

- Atrial tachycardia (+4)
- 2nd degree AV block - Type I (Wenckebach)

Describe the findings and diagnosis:

- EKG
- ST
- Acute Pericarditis
******Patient underwent left pneumonectomy and pericardial resection secondary to malignant mesothelioma. The patient developed post-operative EKG changes consistent with pericarditis.

Describe the findings:

- NSR
- SA exit block
- Nonspecific ST and/or T wave abnormalities