Nuclear - Test Review Flashcards
How often is a dose calibrator checked:
- linearity
quarterly
A bar phantom is used to assess this?
How often is this checked?
- Linearity and Spatial Resolution
- Weekly
What is the equivalent dose of 1 Curie:
- Bq or becquerels
1 Curie = 3.7 x 1010 radioactive decays per second
What is the permissible breakthrough of Molybdenum-99 per mCi of Tc99m?
0.15 microcurie (μCi) of M-99 per 1 mCi of Tc99m
What is the half-life?
- Dobutamine
- Rubidium-82
- N13
- Dobutamine –> 2 minutes
- Rubidium-82 –> 75 seconds
- N13 –> 10 minutes
What radiotracer has the lowest extraction fraction?
Tc99m Tetrofosmin
What radiotracers act as potassium analogs when taken up into the myocardial cells?
- Rubidium
- Thallium
What is the next step:
- LBBB on EKG
- Exercise MPI –> perfusion defect in lateral wall
coronary angiogram
- perfusion defect in lateral wall not septum
What is the diagnosis in a patient with CABG who presents with chest pain and septal ischemia on MPI?
native vessel disease (not graft occlusion)
What can cause clear N13 perfusion images and blurry FDG-F18 metabolism images?
Diabetes
- insulin resistance?
What does gating improve when added to MPI?
specificity
Describe the difference in sensitivty/specificty between MPI radiotracers:
- Tc99m sestamibi
- Tl201 thallium
- Sensitivity –> similiar between the two
-
Specificity –> Tc99m significanty better
- further enhanced by gating
What is the effect on EF if you utilize 8 frames instead of 16 frames?
underestimate of EF
How do vasodilators work in stress testing?
differential hyperemia?
How do vasodilators induce ischemia?
vasodilatation of healthy arteries
Why can’t you image Tc99m and Tl201 at the same time?
Photopeak crossover
A ramp filter will remove this type of artifact?
star artifact
- marked streaking in an area with intense radionuclide emission
What is the effective half life of Tc99m if biological T1/2 = 3 hours?
TE = 1/3 + 1/6
TE = 1 / 0.5
TE = 2
TE = TB + TP
- TE = Effective half life
- TB = Biologic half life
- TP = Physical half life
What interaction occurs at a PMT?
photon converted to an electron
What is the units for diastolic function via MUGA?
end diastolic volumes / second???
How often is constancy checked?
daily
Describe recommendations for RNA (MUGA). Initiating and monitoring Adriamycin (Doxorubicin) therapy

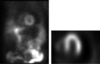
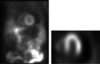
Describe the finding:
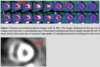
Pericardial effusion

What is the radiotracer for fatty acid metabolism?
C11-Palmitate
What is the effective annual dose limit for the public, infrequent exposure?
1 mSv (100 mRem or 0.1 Rem)
What is the diagnosis if:
- stress perfusion defect
- normal wall motion and EF
ischemia
- patients are imaged a while after stress so the EF recovers
What is the greatest determinant of radiation exposure?
radiotracer half-life
- shorter half life –> lower Sv
- don’t pick lower mCi administered
NTG enhances assessment of viability with which radiotracer?
Tc99m Sestamibi
What is one requirement of radioactive material delivery to a lab?
someone must receive it
What is the most frequently used radiotracer for linearity dose calibration?
Tc99m (Sestamibi)
If exposure rate is 1R / hr at 1 meter
What is the exposure rate at 3 meters?
0.111
I1 (d1)2 = I2 (d2)2
1 = I2 (9)
1 / 9 = I2
I2 = 0.1111
-
Inverse square law
- intensity (exposure, I1) = 1 / d2
- I1 (d1)2 = I2 (d2)2
How should the inverse square law be applied in patients with two separate distances and a set dose rate?
I1 (d1)2 = I2 (d2)2
Where is Tc99m sestamibi incorporated in the cell?
mitochondria
What chamber is used for dose calibration?
ionization chamber
What is the diagnosis of a hot spot in the LV cavity near the left lateral wall on SPECT?
papillary muscle
What happens to LVEF on MUGA if the background is over the spleen?
overestimated LVEF
What is the diagnosis of a patient with LAD and RCA stents presenting with chest pain?
MPI SPECT with ischemia in the anterolateral wall?
progressive disease of the RI
***Diagonal not a choice
What is the next step:
Patient preesents to ED with chest pain –> rest spect performed at this time shows AC corrected images with inferior defect
coronary angiogram
ERNA relies on this?
uniform labeling of the blood pool
Where is spatial resolution best in regards to the collimator?
at the face of the collimator
When can you dispose of radioactive waste?
when activity is similar to background radiation
Which Butterworth filter produces the most noise?
one with the highest frequency allowed
What is the effect as you move away from a collimator:
- Sensitivity
- Count density
- Resolution
- Sensitivity and Counts –> remain the same
- Resolution –> decreases
In the in vivo method of RBC labeling, when are stannous pyrophosphate and Tc99m pertechnetate injected?
Stannous pyrophosphate
given ~20 minutes prior to
Tc99m pertechnetate
What is one finding seen on patients with ASD repair?
Why?
Paradoxical septal motion
prior open heart surgery
What is the bias when a lab has:
- high sensitivity
- low specificity (40%)
Post-referral bias
- occurs when patients with abnormal stress test results are referred to cardiac catheterization at a higher rate than are patients with normal stress test results
What are the best radiotracers for quantitating myocardial blood flow and perfusion?
- O15
- N13
Describe the ischemic cascade
- Perfusion abnormalities
- Diastolic Dysfunction
- Strain abnormalities
- Systolic dysfunction
- EKG abnormalities
- Angina

In the setting of acute MI what does a perfusion defect on rest SPECT represent?
Infarct; Ischemia; Stunning; Area at risk.???
What scale should always be utilized for interpretation of SPECT?
Linear scale
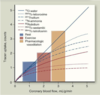
What is the downside of sigmoidal (nonlinear) vs. linear scales?
- gradual changes in uptake are seen better than when using sigmoidal (nonliear scales)
- small defects may be missed
When are logarithmic scales utilized?
regions with lower count density (RV)
- not used for evaluation of regional differences in LV tracer uptake
The principle of thickening assessment in gated SPECT images from end-diastole (count poor) to end-sytole (count rich) is based on what principle?
Partial volume averaging
- basis of assessing thickening of myocardial segments is based on the brightening between end-diastolic to end-systolic images related to partial-volume effect reflective of the limitations of spatial resolution of the gamma camera
- This results in relative increase in count intensity manifested as brightening used by different vendor programs to quantitate degree of thickening
Selective use of angiography after SPECT imaging as compared to direct angiography in patients with stable angina results in:
What is the effect of mortality/outcomes/cost?
lower cost
- END study
- showed that cost was significantly reduced in those who underwent cath-only based on MPI results
- direct catheterization group –>
- same mortality
- higher cost
When performing a dipyridamole stress MPI study, after the 4-minute dipyridamole infusion, what is the recommended time delay before injecting the radiotracer?
5 minutes
- maximum vasodilation of dipyridamole is 287 +/- 101 seconds
- radiotracer injection should not be injected until 3-5 minutes following dipyridamole injection
What tools/activities provide the greatest improvement in appropriate use of MPI?
- Clinician feedback regarding performance
- Clinical decision support tools
- probably the most powerful
What will be the result of increasing the number of frames from 8 to 16 in a gated MPI study (leaving all other parameters the same)?
decrease the counts per frame
- because the set number of counts are divided into double the number of frames
- there is a decrease in the counts per frame
What is the affect on the following as a result of increasing the number of frames from 8 to 16 in a gated MPI study (leaving all other parameters the same)?
- Temporal resolution
- Spatial Resolution
- Counts per frame
- Ejection fraction
- Temporal resolution –> increase
- more points sampled over a period of time
- Spatial Resolution –> unchanged
- Counts per frame –> decrease
- set number of counts divided by a double number of frames
- Ejection fraction –> increase
Describe the findings and next step:
- 45 year old male with pleuritic chest pain after exertion
- Serial EKG/Troponin negative
- Resting MPI (while having active chest pain) with LVEF 60%

discharge and plan elective outpatient stress imaging
- Resting images –> no perfusion defects
- while having active chest pain –> nonischemic etiology
What study supports acute rest MPI studies in the ER?
ERASE
- normal perfusion –> very low event rate
- can be safely and quickly triaged for discharge
What are the recommended (ASNC guidelines) acquisition parameters when using a conventional SPECT system to acquire a MPI study utilizing Tc99m tetrofosmin:
- Collimator
- Seconds per step
- Energy window on PHA
- Frames per cardiac cycle
- Collimator –> Low-energy, High-Resolution (LEHR) collimator
- Seconds per step –> 20s / step
- Energy window on PHA –> 20% energy window
- Frames per cardiac cycle –> 8 frames per cardiac cycle
Describe the findings and next step:
- 50 year old male training for a marathon, presents for abnormal EKG: RBBB
- Exercise SPECT: 1 mm ST depression at peak exercise x 12 minutes. EF 61% –> 62%, TID 1.13

cardiac catheterization
- SPECT: perfusion abnormalities in septum from base to apex
- likely proximal LAD disease
- Exercise capacity good but EKG changes of ischemia
- patient training for a high-intensity event
What is the minimum time interval after the VQ scan when a stress Tc99m sestamibi MPI scan can be performed?
24 hours
- half-life = 6 hours
- 4 half lives = 24 hours
- this number of half-lives should elapse between studies with similar tracers

B - 49 yo DM male with atypical CP and CAC > 100
- appropriate to perform a seqeuential stress RNI for those patients with a prior abnormal CCT calcium and agtston > 100
What is the cause of the septal defect:
- EKG: LBBB
- SPECT: fixed septal defect, EF 58%, HR 64 –> 78
- CTA: no CAD

Partial volume effects
- Hayat et al. study
- patients with LBBB + no CAD –> reduced septal thickness and thickening compared to posterior wall
- resting MBF was preserved
- partial volume effects + limited spatial resolution of SPECT (10-12mm) –> areas with end-diastolic thickness < 10 mm show perfusion defects
- as the count intensity changes in systole dictates thickening assessment, asymmetric reductions in septal thickening during systole observed in LBBB reduced recovery coefficients of detected counts –> accounts for the septal defect at rest unrelated to HR

What is the difference in septal defects associated with LBBB in vasodilator and stress MPI?
- Exercise –> reversible septal defect
- HR related decrease in blood flow
- Vasodilator –> fixed septal defect
- partial volume effects + decreased spatial resolution
What is a disadvantage of new solid-state cameras compared to conventional (A-SPECT) cameras?
Incidence of diaphragmatic attenuation
- likely due to higher resolution of the cameras and artifact associated with breathing
- respiratory gating has been shown to help
What are the radiotracers utilized for:
- ATTR
- AL
- ATTR –> Tc99m pyrophosphate (PYP)
- AL –> F18 florbetapir
- taken up by both AL and ATTR amyloid but cannot distinguish between the two
Where is the greatest response to vasodilatory stimuli seen?
coronary arterioles
- most responsive as they possess smooth muscle
- venules have less vasodilatory capacity and capillaries do not possess smooth muscle
Describe coronary microcirculatory physiology as it relates to
- myocardial blood volume
- myocardial perfusion defects
- at rest approximately 90% of myocardial blood volume is in capillaries and
- capillary resistance is the primary determinant of coronary vascular resistance
- Perfusion defects (on SPECT) are primarily felt to be related to elevation of capillary resistance and reduction in myocardial blood volume at the capillary level
- This leads to reduced isotope uptake due to capillary decruitment, which happens in response to epicardial coronary stenosis

C - 55 yo woman, BMI 44, no cardiac history, new SOB
- 2 day protocol is best used in the patient with large body habitus where high-dose stress-and-rest imaging could provide image quality for diagnostic purposes
- mainly reserved for large BMI

B - 2 day high-dose stress, high-dose rest exercise MPI
- No limitations for exercise
- Imaging is appropriate –> baseline ST, T changes
- High BMI ( > 35 ) –> 2-day high/high is protocol is recommended

D - asymptomatic woman with anomalous RCA from left cusp with interarterial course
- interarterial course –> high risk for sudden death
- recommend evaluating for provocable ischemia with imaging
What is the recommended stress testing for a patient with:
- mild, chronic stable angina and a small, mild perfusion defect two years ago
no testing
- chronic stable angina + mild ischemia (on SPECT) + no change in symptomatology –> continue medical management