Anatomy - Thorax / Asthma Flashcards
(233 cards)
What is the purpose of costal cartilage?
Provides resilience and stability
What are these parts called?


What are these lines called?

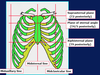
What are the properties of intercostal muscles?
In intercostal space
3 layers - external, internal, innermost
Respiration importance
Help keep intercostal space rigid
Where is pleura found and what are the 2 types?
Each lung is enclosed in serous pleural sac
2 continuous membranes - visceral (surface) and parietal (inner surface – lines pulmonary cavities)
What are these parts called?


What is a health problem related to the thorax?
Thoracic outlet syndrome - where important arteries and nerves are compressed
What are the 2 thoracic apertures and their function?

What number are these atypical ribs?


What are these parts called?


What is the purpose of the scalene tubercule on rib 1?
Where scalene anterior muscle attaches
Where does the pectoralis major attach to?
Clavicular head which attaches to clavicle
Sternocostal head which attaches to sternum + upper 6 costal cartilages
Fibres which converge on intertubercular groove or humerus
What is the function of the pectoralis major?
- Adductor and medial rotator of arm at shoulder joint
- Can act also as flexor (when arm extended) and as extensor (when arm flexed)
- If pectoral girdle is ‘fixed’, it can act also as an accessory muscle of respiration
Which nerves innervate the pectoralis major?
Medial and lateral pectoral nerves (C5-8 and T1)
Where does the pectoralis minor attach to?
Coracoid process of scapula, ribs 3-5 near cartilage
What is the function of the pectoralis minor?
Depressor of scapula (and, hence, shoulder) and protractor of scapula
If pectoral girdle is ‘fixed’, it can act also as an accessory muscle of respiration
Which nerve innervates the pectoralis minor?
Medial pectoral nerve (C8 and T1)
What are these parts called?


What is the mediastinum?
Central part of thoracic cavity, between pleural cavities
What are the boundaries of th mediastinum?
Sternum (anterior)
Thoracic vertebral column (posteriorly)
Thoracic inlet and root of the neck (superiorly)
Diaphragm (inferiorly)
What are these parts called?


What are the contents superior mediastinum?
- Thymus (lymphoid organ; large between birth and puberty but involutes in adult, especially after disease);
- Great veins (SVC, brachiocephalic vv);
- Phrenic nerves;
- Arch of aorta and branches;
- Origins of internal thoracic arteries;
- Pulmonary aa and vv;
- Vagus nn;
- Recurrent laryngeal branches;
- Trachea (lower half) and bifurcation into main bronchi (T4/5 in expiration); Oesophagus;
- Thoracic duct
What are the divisions are the mediastinum?
Superior and inferior –> behind manubrium sterni and behind body and xiphoid process of sternum
What are these parts called?