HNS 1 Flashcards
(127 cards)
What structure is being pointed at here?

bregma
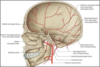
What is the biggest venous sinus?
Superior saggital sinus
Advantage of the anterior fontanelles?
Bones haven’t fused yet, gives skull a little flexibility in case the birth canal is too tight
Which suture does the sphenoid bone articulate with the squamous part of the temporal bone?
Sphenosquamous suture
Which 2 main artery systems form the Circle of Willis?
Internal carotid arteries
Vertebral arteries
Which bones articulate with the squamous part of the temporal bone?

Greater wing of sphenoid
Parietal bone at the squamous suture

Which bone does the temporal bone articulate posteriorly with?
Occipital bone
Which foramen does the facial nerve and vestibucochlear nerve + where is it on the diagram?

Internal acoustic meatus

What are the 8 branches of the external carotid artery?
Superior thyroid artery
Ascending pharyngeal artery
Lingual artery
Facial artery
Occipital artery
Posterior auricular artery
Maxillary artery
Superficial temporal artery
Describe characteristics of the pia mater
Innermost, thin + delicate layer
How does this artery enter the cranial fossa?

Foramen spinosum
Which foramen is associated with mandibular nerve + where is it on the diagram?

Foramen ovale

Which layer is closely adherent to the brain?
The pia mater
Which arteries supply the anterior cranial fossa + where is on the diagram?

Anterior meningeal arteries

Which structures of the brain are found within the posterior cranial fossa?
Cerebellum and brainstem

Which bones form the floor of the posterior cranial fossa?
Occipital bone
Temporal bone

How can you identify an extradural haematoma on a CT scan?
More focal
Does not extend beyond suture
Bi-convex (lens shaped)

What is the falx cerebri?
Falx cerebri is a crescent shaped downward projections of meningeal dura mater from the dura lining the calva that passes between the two cerebral hemispheres towards the corpus callosum.
Helps stabilise the brain within the cranial cavity
What structure is being pointed to?

Pterion
Name the different coloured structures

Green = frontal bone
Blue = sphenoid bone
Dark pink = nasal bone
Light pink = maxilla
Orange = zygomatic bone
Purple = mandible
Red = vomer
What is the highlighted bone?

Zygomatic process
Which foramen does the accessory nerve pass through?
Jugular foramen
Which part of the temporal bone has a flat plate appearance and forms the superior regions of the temporal bone?
Squamous part
What is a subdural bleed?
Deep to the dura