HNS 3 Flashcards
(172 cards)
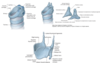
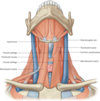
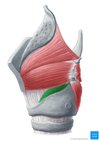
label this diagram

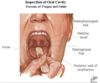
What nerve are doctors testing when asking a patient to open their mouth (ah)?
Vagus nerve
Which cranial nerve provides motor functions to the uvula?
Vagus nerve
What would you expect to see of the uvula if vagus nerve functioning normally (when testing it clinically)?
Uvula should go straight up the midline
A lesion to the right vagal nerve of the uvula results in what deviation?
Deviation to the opposing side
What does a deviation of the uvula to one side suggest?
Problem with one of the vagus nerves
Uvula deviates away from the side where the lesion is
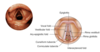
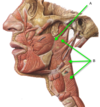
What pharynx is posterior to the oral cavity?
Oropharynx
Can see posterior wall of oropharynx behind the uvula in image shown
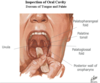
What is the palatoglossal fold?
Most anterior fold of tissue at back of mouth
From the palate at the top of the mouth down to the tongue
What is the palatopharyngeal fold?
Posterior to the palatoglossal fold
From the palette to the pharynx
What is the palatine tonsil?
In between the palatoglossal fold and the palatopharyngeal fold
What do the tonsils give you an idea of?
If there’s been infection or inflammation
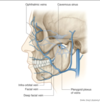
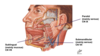
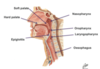
Label the diagram and what view of the head is it?

Mid-saggital view
How does the hard palate assist eating?
Tongue is used to move food up against the hard palate to start breaking it down
What hangs from the soft palate?
The uvula
What 3 structures form the pharynx?
Nasopharynx
Oropharynx
Laryngopharynx
Function of the epiglottis?
Retroflexes over laryngeal inlet when you swallow food, preventing food going down into airways
Allows food to travel down back of pharynx down to oesophagus
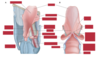
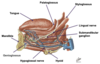
Label this diagram


Where does the tongue sit?
Buccal cavity
What does the epiglottis cover?
Laryngeal inlet
What is the piriform fossa?
Area has quite a strong sensory innervation where you can get bits of bones stuck
Channel that directs solid & liquids from oral cavity around the raised laryngeal inlet and into the oesophagus
Sensitive are that can cause distress to someone that gets something caught there
What are the muscles of the pharynx?
Superior, middle and inferior constrictors
Which 2 nerves form the pharyngeal plexus and what does it provide?
Glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves (strong sensory innervation)
Strong sensory innervation to the muscles of the pharynx
Which nerve controls the motor functions of the constrictors?
Vagus nerve (CN10) + accessory nerve (XI)
What is the action of swallowing?
Coordinated sequential contraction of superior, middle and inferior constrictors
Allows coordinated contraction of food bolus from mouth down to oesophagus