UL extra Flashcards
(136 cards)
What are the joints that make up the pectoral girdle?
- clavicle and sternum (sterno-clavicular)
- clavicle and scapular (acromio-clavicular)
- scapula + humerus (gleno-humeral)
- scapula + thoracic wall (scapulo-thoracic)
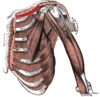
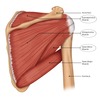
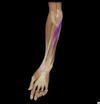
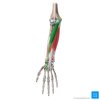
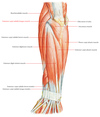
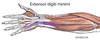
Label the image


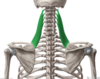
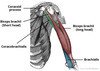
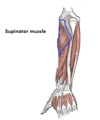
Label this image
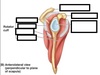

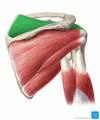
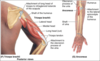
Label this image


What does the glenoid labrum do?
Deepens the glenoid fossa to stabilise the shoulder
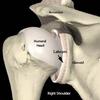
What are the different muscle compartments of the shoulder?
Anterior pectoral girdle
Posterior pectoral girdle
Intrinsic shoulder muscles
What muscles are contained in the anterior pectoral girdle?
pectoralis major
pectoralis minor
subclavius
serratus anterior
what muscles are contained in the posterior pectoral girdle?
trapezius
levator scapulae
latissimus dorsi
rhomboid major
rhomboid minor
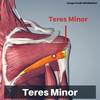
what are the intrinsic shoulder muscles?
- deltoid
- teres major
- supraspinatus
- infraspinatus
- teres minor
- subscapularis
What are the two muscle groups that serve the shoulder region?
- pectoral girdle
- intrinsic shoulder muscles
What are the 4 surrounding ligaments that stabilise the glenohumeral joint?
glenohumeral ligaments
coracohumeral ligaments
transverse humeral ligaments
coracoacromial ligaments
What does the glenohumeral ligament do?
stabilises the anterior aspect of the joint and prevents it dislocating anteriorly

what does the coracohumeral ligament do?
attaches the coracoid process to the greater tubercle of humerus, supporting superior part of joint capsule

what does the transverse ligament do?
connects greater and lesser tubercles holding tendon of long head biceps brachia in place

what does the coracoacromial ligament do?
spans between acromion and coracoid prcoess forming coracoacromial arch
overlies shoulder joint and prevents superior displacement of humeral head

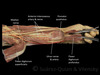
Label this image of ligaments


What is the pectoral region of the anterior chest wall?
contains 4 muscles that exert a force on the upper limb
pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, serratus anterior + subclavius
what is the pectoralis major muscle?
most superficial muscle in the pectoral region
large + fan shaped
has sternal head + clavicular head (sternal orginiates from anterior surface of the sternum, clavicle originates from the anterior surface of the medial clavicle)
distal attachment of both heads is into the intertubercular sulcus of humerus

Function of pectoralis major + innervation?
adducts + medially rotates the upper limb
draws scapula anteroinferiorly
clavicular head acts individually to flex upper limb
innervated by medial and lateral pectoral nerves
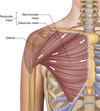
What is the pectoralis minor?
lies underneath the pectoralis major
both muscles form part of anterior wall of axilla region
originates from 3rd-5th ribs and inserts into coracoid process of scapula

function + innervation of pectoralis minor?
stabilises scapula by drawing it anteroinferiorly against thoracic wall
median pectoral nerve
what is the serratus anterior?
located more laterally in chest wall
consists of several strips -> originate from lateral aspects of ribs 1-8 and attach to costal surface of medial border of scapula

function + innervation of serratus anterior?
Rotates the scapula, allowing the arm to be raised over 90 degrees. It also holds the scapula against the ribcage.
long thoracic nerve

What is the subclavius muscle?
small muscle directly underneath the clavicle -> offers minor protection to underlying neurovascular structures
originates from junction of 1st rib and its costal cartilage -> inserts into inferior surface of middle third of the clavicle