HNS 2 Flashcards
(209 cards)
What are the 3 main functions of the neck?
Structural: supports and moves the head
Visceral: contains the trachea and oesophagus
Conduit for blood vessels and nerves
Principle arterial supply of the head and neck?
Carotid arteries
What is fascia?
A connective tissue mainly composed of collagen fibres
Organises the body into different compartments
Why is the fascia clinically important?
Permits the spread of infection within compartments
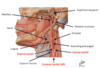
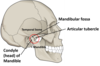
What is the most external fascial layer in the neck and what does it contain?
Superficial fascia
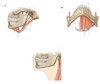
Contains the platysma muscle at the front of the neck
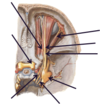
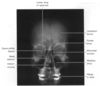
Where on this diagram is the platysma muscle?
Anterior to the neck

What is the platysma innervated by?
Cervical branch of facial nerve
What are the 3 main compartments of the neck?
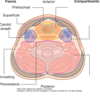
Visceral compartment
Vertebral compartment
Vascular compartment

What is deep to the superficial fascia?
Deep fascia
What layers are the deep fascia divided into?
Pretracheal fascia
Carotid sheath
Investing fascia
Prevertebral fascia
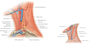
What does the pretracheal fascia surround?
Some of the visceral components of the neck
We can find some of the components of the digestive system and respiratory system + endocringe glands
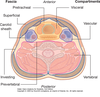
Where is oesophagus in relation to trachea?
Oesophagus is posterior to the trachea
Which structures reside within the visceral compartments?
Oesophagus, trachea, pharynx + thyroid gland
What is deep fascia?
Dense, organised connective tissue deep to the superficial fascia
Organised into distinct layers:
- Carotid sheath
- Pretracheal fascia
- Investing fascia
- Prevertebral fascia
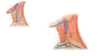
What is the carotid sheath and where is it on the diagram?
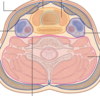
Fascia that surrounds the:
- common carotid artery
- internal jugular vein
- internal carotid artery
- vagus nerve
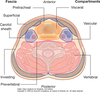
What does the investing layer of fascia contain?
- Sternocleidomastoid muscle
- Trapezius muscle
- Infrahyoid muscles
What structures are contained in the prevertebral layer + function?
- Spinal cord
- Deep muscles of the back
- Anterior, posterior + middle scalene muscles
Contains a number of muscles which help move + stabilise the ehad
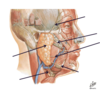
What are the 2 main triangles of the neck?
Anterior triangle
Posterior triangle
What divides the 2 muscles of the neck + where does it go from and to?
Sternocleidomastoid muscle
From the skull down to the sternum + clavicle
What are the boundaries of the anterior triangle?
- Inferior margin of the mandible (superior)
- Anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle (posterior)
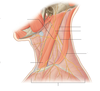
Label diagram of the neck
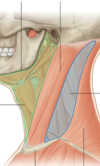

Boundaries of the posterior triangle?
Posterior aspect of the sternocleidomastoid muscle
Anterior aspect = anterior aspect of the trapezius muscle
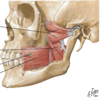
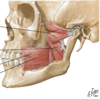
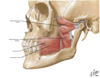
What muscles are contained in the anterior triangle of the neck?
Platysma muscle
Suprahyoid muscles (mylohyoid, geniohyoid, digastric + stylohyoid muscles)
Infrahyoid muscles (omohyoid, sternohyoid, thyrohyoid + sternothyroid muscle)
What blood vessels are contained in the anterior triangle of the neck?
Internal jugular vein
Common carotid artery
Internal carotid artery