L13 & 14: Endocrine Pancreas & Diabetes Flashcards
(60 cards)
The pancreas develops embryologically as an outgrowth of…?
Foregut
State the exocrine and endocrine function of the pancreas
- Exocrine (99%): produces digestive enzymes and secretes them directly into duodenum via pancreatic duct
- Endocrine (1%): hormone production from Islet of Lanerhans
Within an Islet of Langerhans, state where:
- alpha
- beta
…cells are found
- Alpha cells: periphery
- Beta cells: central
*Others are scattered and in smaller numbers
What cells, in Islet of Langerhans, secrete insulin?
Beta
What cells, in Islet of Langerhans, secrete glucagon?
Alpha
What cells, in Islet of Langerhans, secrete somatostatin?
Delta
What cells, in Islet of Langerhans, secrete pancreatic polypeptide?
PP cells
What cells, in Islet of Langerhans, secrete grehlin?
e cells
What cells, in Islet of Langerhans, secrete gastrin?
G cells
What cells, in Islet of Langerhans, secrete vasoactive intestinal peptide?
VIP cells
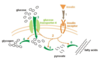
What does this image show?

Islet of Langerhans
State the role of:
- Insulin
- Glucagon
- Insulin: lowers blood glucose levels
- Glucagon: increase blood glucose levels

Are glucagon and insulin water or lipid solube?
Water. Travel in blood and then react with cell surface receptors on target cells. Receptor, with hormone bound, can then be internalised- hormone then inactivated.
What’s the half life of glucagon and insulin?
5 minutes
Which organ in body uses glucose at fastest rate?
Brain so it is very sensitve to changes in glucose concentration
What can high plasma glucose do to cells? (think about deformation)
Cause water to move out of cells so they shrivel
For insulin and glucagon, compare and contrast:
- What state it says the body is in
- Target tissues
- Which ‘food groups’ it affects metabolism of
- Anabolic or catabolic

State the expected plasma glucose concentrations when:
- Normal
- After a meal
- Renal threshold
- Normal: 3.3-6mmol/L
- After meal: 7-8mmol/L
- Renal threshold: 10mmol/L
What happens if plasma glucose is above renal threshold?
State two factors which can affect renal threshold
Kidneys excrete glucose in urine - glycosuria
- Pregnancy decrease
- Elderly increase
Insulin is anabolic and anti-gluconeogenic; what do we mean by anti-gluconeogenic?
Lower incorporation of pyruvate into gluconeogenesis but stimulates pyruvates incorporation into glycogen
Describe structure of insulin
- Alpha helix
- 2 unbranched polypeptides (A & B)
- 2 disulphide bonds between A & B chains
- 1 intrachain disulphide bond in A chain
- C peptide between A & B chains

Is C peptide found in circulating insulin?
No as it is removed by golgi before secretion
Describe how insulin is produced and prepared for release in beta cells
- Insulin sotred in secretory granules as crystalline zinc-insulin complex
- Secretory vesicles contain equimolar amounts of insulin and C peptide

What can a measure of C peptide in plasma tell us?
Amount of endogenous insulin secreted (released in equimolar amounts)