L15: HPA Axis & GH Flashcards
(35 cards)
What is the hypothalamic pituitary axis?
Functional unit, compromising hypothalamus and pituitary gland, which serves as a major link between endocrine and nervous systems
Where is the pituitary gland located?
Beneath hypothalamus in socket of the sella turcica bone at base of skull

State the two parts of the pituitary gland and for each state its embryonic origin
- Anterior (adenohypophysis): evagination of oral ectoderm (Rathke’s pouch)- upward growth
- Posterior (neurohypophysis): neuroectoderm/primitive brain tissue- downward grwoth
How do axons pass from hypothalamus to posterior pituitary?
Pituitary stalk (infundibulum)

State another name for:
- Anterior pituitary
- Posterior pituitary
- Anterior: adenohypophysis
- Posterior: neurohypophysis
State some processes modulated by hypothalamus and pituitary gland

Describe the relationship between hypothalamus and anterior pituitary, include:
- What signals are sent
- How they are sent
- Consequences of signal
Hormones produced in hypothalamus control hormone production and secretion in anterior pituitary:
- Hormones synthesised hypothalamus in neurosecretoy cells
- Transported down axons and stored in median eminence
- When ready, released into hypophyseal portal system
- Hormones stimulate or inhibit endocrine cells in anterior pituitary by binding to GPCRs on surface
- Anterior pituitary produces and secretes hormones to distal and neighbouring cells

Striclty speaking, is the posterior pituitary a gland?
No, as it doesn’t produce the hormone it secretes
Describe how ADH & oxytocin are produced and released
- Produced in neurosecretory cells in supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of hypothalamus
- Transported down axons (via pituitary stalk/infundibulum) to posterior pituitary (axons merge with capillary bed)
- Stored and released by posterior pituitary, when required, into general circulation to distant targets. Release is regulated by neuronal inputs to hypothalamus
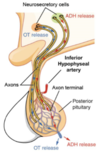
Posterior pituitary contains axons which originated in hypothalamus and some specialised glial cells called…?
Pituitcytes
Describe the actions of ADH
- ADH: binds to receptors on epithelium of collecting ducts of kidneys and induces translocation of aquaporins to increase water reabsorption. Can also bind to receptors on smooth muscle cells in vasculature to cause vasoconstriction. Osmoreceptors in hypothalamus detect changes in plasma osmolality to control ADH release
Describe the actions of oxytocin
- Oxytocin: suckling stimulates reflex in which signals from breast to hypothalamus cause release of oxytocin. Binds to receptors on myoepithelial cells in mammary glands causing contraction to squeeze milk out. Also released in childbirth due to pressure on cervix as can bind to smooth muscle cells in uterus causing contractions.
State 2 hormones produced by hypothalamus but released by posterior pituitary
- ADH
- Oxytocin
State 7 tropic hormones produced and released by hypothalamus into hypophyseal system to control release of anterior pituitary hormones
All are TROPIC hormones

- *RH= releasing/stimulating*
- *IH= inhibitory*
State the name and role of 6 hormones produced and released by anterior pituitary

Give a summary of effects of hormones involved in the hypothalamus & anterior pituitary system (think flow diagram)

Does PRH (prolactin releasing hormone) play a major role in controling prolactin secretion?
No, its stimulatory effects don’t account for much of the regulation. A lot of the regultation comes from dopamine (PIH= prolactin release-inhibiting hormone); decrease levels to increase release and vice versa
Define:
- Necrosis
- Apoptosis
- Atrophy
- Hyperplasia
- Hypertrophy

Hormone production in both hypothalamus and anterior pituitary is regulated by negative feedback; describe the types of loops in this negative feedback
- Ultrashort: hormone released by hypothalamus feeds back
- Short: hormone produced by anterior pituitary feeds back
- Direct long: hormone produced by target endocrine tissue feeds back to anterior pituitary
- Indirect long loop: hormone produced by target endocrine tissue feeds back to hypothalamus

Which cells, in anterior pituitary, produce growth hormone?
Somatotrope cells
Describe the circadian rhythm of growth hormone
GH released in pulsatile fashion, with circadian rhythm, with maximal release at night
Describe what is meant by direct and indirect effects of growth hormone
Exerts direct effects as GH; exerts indirect effects as it stimulates production of insulin-like growth factor (also called somatomedins, IGF1 & IGF2) in liver & skeletal muscle
Describe the effects of growth hormone and IGFs in children and in adults

Secretion of GH can be regulated by CNS (via inputs to hypothalamus) or metabolically. Describe some things that
a. ) Increase GH secretion
b. ) Decrease GH secretoin
Blue= CNS inputs
Green= metabolic




